Apricitabine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
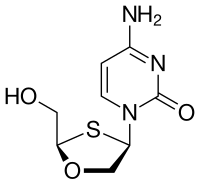
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Apricitabine | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 11 N 3 O 3 S | |||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action | ||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 229.26 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Apricitabine (SPD754, AVX754) is an experimental drug used to treat HIV- infected patients as part of combination therapy for HIV .
It belongs to the group of nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs).
history
Apricitabine is currently being developed and tested by Avexa Pharmaceuticals , an Australian pharmaceutical company. Phase IIb studies were completed in 2006.
The active ingredient was originally developed by BioChem Pharma as BCH10618. After being sold to Shire Pharmaceuticals , the active ingredient was renamed SPD754. Shire then sold the rights to Avexa (AVX754).
pharmacology
Apricitabine has been examined in various studies. The result of the studies is that with apricitabine monotherapy the best virus suppression was achieved at a dose of 1200 mg. The active ingredient was able to reduce the viral load by up to 1.65 log levels.
The similarity to the active ingredients lamivudine (Epivir ® ) and emtricitabine (Emtriva ® ) makes a combination with them pointless.
Pharmacokinetics
Apricitabine was rapidly absorbed in studies and mainly renal metabolized. The highest plasma levels are reached after 1.5 to 2.5 hours.
Side effects
In previous studies, apricitabine was well tolerated.
Resistances
No therapy-induced resistance mutations were observed in the previous studies.
In vitro apricitabine showed good activity against NRTI-resistant strains (including zidovudine (Retrovir ® ) and lamivudine (Epivir ® )). Previous studies showed that apricitabine was also effective against strains that were resistant to Epivir. New studies show that the active ingredient K65R mutations can cause resistance to didanosine (Videx ® ) and tenofovir (Viread ® ).
Future studies will have to clarify whether the active ingredient is actually responsible for the K65R mutation.
Individual evidence
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Avexa and Novasep announce signing of contract for the production of apricitabine .
- ↑ a b c Apricitabine (Aidsmeds) ( Memento of the original from March 21, 2008 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. .
- ↑ a b c P. Cahn, I. Cassetti, R. Wood, P. Phanuphak, L. Shiveley, RC Bethell, J. Sawyer: Efficacy and tolerability of 10-day monotherapy with apricitabine in antiretroviral-naive, HIV-infected patients . In: AIDS . 20 (9), Jun 12, 2006, pp. 1261-1268. PMID 16816554 .
- ↑ P. Cahn, M. Rolon, I. Cassetti, L. Shiveley, T. Holdich, J. Sawyer: Multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of apricitabine, a novel nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor, in patients with HIV-1 infection. In: Clin Drug Investig. 28 (2), 2008, pp. 129-138. PMID 18211121 .