Baeyer pyridine synthesis
The Baeyer pyridine synthesis , named after the German chemist Adolf von Baeyer , is a name reaction from the field of organic chemistry and was first described in 1910. With the Baeyer pyridine synthesis, pyran derivatives and pyrone derivatives can be converted into pyridine derivatives.
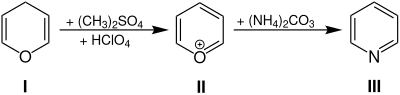
Overview reaction
Pyran I is first reacted with dimethyl sulfate and perchloric acid to form an oxonium salt . The oxonium II then reacts with derivatives of ammonia to form pyridine III .
Reaction mechanism
The following mechanism is described in the literature:
In the first step of the synthesis, the amine attaches itself to the aromatic ring of oxonium 1 , which leads to a ring opening and compound 2 is formed. An electron rearrangement occurs, whereby the free electron pair of the nitrogen can then close the ring again and compound 3 is formed. By dehydration resulting pyridinium 4 . A nucleophilic attack finally deprotonates, creating pyridine ( 5 ).
further reading
- Karl Dimroth: Newer Methods of Preparative Organic Chemistry III. 3. Aromatic compounds from pyrylium salts In: Angewandte Chemie . 72, 1960, pp. 331-358, doi: 10.1002 / anie.19600721002 .
- Alexandru T. Balaban and Costin D. Nenitzescu: Aluminum chloride catalysis, XXVII A synthesis of pyrylium salts from acid chlorides and olefins In: European Journal of Organic Chemistry . 625, 1959, pp. 74-88, doi: 10.1002 / jlac.19596250110 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Adolf Baeyer: On the action of dimethyl sulfate on dimethyl pyrone In: Ber. German Chem. Ges. 43, 1910, pp. 2337-2343, doi: 10.1002 / cber.191004302198 .
- ^ Dear F. Cavalieri: The Chemistry of the Monocyclic α-and γ-Pyrones In: Chem. Rev. 41, 1947, pp. 525-584, doi: 10.1021 / cr60130a004 .
- ↑ Alfred Hassner and Irishi Namboothiri: Organic Synthesis Based on Reaction name , Elsevier, 2012, ISBN 978-0-08-096630-4 , p. 30
- ^ A b Zerong Wang: Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents , Wiley, 2009, ISBN 978-0-471-70450-8 , pp. 147-149.
- ↑ Alan R. Katritzky and Dr. Charles M. Marson: Pyrylium salts as intermediates in the conversion of NH2 groups into other functional groups In: Angewandte Chemie . 96, 1984, pp. 3039-3071, doi: 10.1002 / anie.19840960605 .