Pyrans
| Pyrans | |||
| Surname | 2 H -pyran | 4 H -pyran | |
| other names | α-pyran oxa-2,4-cyclohexadiene |
γ-pyran oxa-2,5-cyclohexadiene |
|
| Structural formula |  |
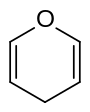
|
|
| CAS number | 289-66-7 | 289-65-6 | |
| 31441-32-4 (unspecified) | |||
| Molecular formula | C 5 H 6 O | ||
| Molar mass | 82.1 g mol −1 | ||
Pyrans are two chemical compounds with the empirical formula C 5 H 6 O that belong to the oxygen-containing heterocycles . Its ring structure is made up of five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom and contains two double bonds . This results in two isomers, the 2 H -pyran or α-pyran and the 4 H -pyran or γ-pyran . Pyrans are not aromatic because not all carbon atoms are sp 2 - hybridized .
γ-Pyran is a colorless oil with a boiling point of 80 ° C, which is soluble in ethanol , benzene and diethyl ether and quickly turns brown in air. The synthesis starts from glutaraldehyde .
Similar structures are formed by some carbohydrates ( sugars ), these are called pyranoses , but do not contain any double bonds in the ring.
Both 2 H -pyran and 4 H -pyran do not occur freely in nature, but many natural substances such as pyrones , such as coumarin or colored flavones , e.g. B. Luteolin . Some synthetic dyes and drugs are also pyran derivatives.
Related links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on Pyrans. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 13, 2014.