Luteolin
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
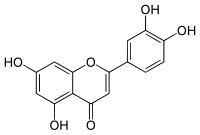
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Luteolin | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 15 H 10 O 6 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
yellowish solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 286.24 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
326-330 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Like many other yellow plant dyes, Luteolin belongs to the flavone family .
Occurrence
Luteolin is found in the reseda plant , dyer's gorse , parsley and artichoke leaves . It is also found in navel oranges , carrots , celery , olive oil , green pepper , chamomile , peppermint , perilla , thyme , rosemary, and oregano .
properties
In its pure form, Luteolin forms yellow, shiny crystals. It is poorly soluble in water.
Effects and side effects
Luteolin promotes sleep due to its property as an agonist at adenosine receptors of types A1 and A2A. Luteolin also has the rare property of increasing the plasmalemmal transport of monoamines .
Like other flavonoids, luteolin has an antioxidant , anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effect in animal experiments . It inhibits interleukin 6 (IL-6 inhibitors) and phosphodiesterase 4 ( PDE4 inhibitors ). It is also said to have positive effects on carbohydrate metabolism and an anti-carcinogenic effect, although these have not yet been scientifically proven in humans. Studies have shown that it similar to allopurinol , the xanthine oxidase inhibiting and thus hyperuricemia and consequent gout can counteract.
The side effects that can occur usually affect the digestive tract. The main symptoms are nausea and vomiting.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on LUTEOLIN in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on March 23, 2020.
- ↑ a b c d Luteolin data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 8, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ^ Albert Gossauer: Structure and reactivity of biomolecules , Verlag Helvetica Chimica Acta, Zurich, 2006, pp. 420-422, ISBN 978-3-906390-29-1 .
- ^ Albert Gossauer: Structure and reactivity of biomolecules , Verlag Helvetica Chimica Acta, Zurich, 2006, p. 422, ISBN 978-3-906390-29-1 .
- ↑ PhytoDoc: Artichoke
- ↑ Kayoko Shimoi, Hisae Okada, Michiyo Furugori, Toshinao Goda, Sachiko Takase, Masayuki Suzuki, Yukihiko Hara, Hiroyo Yamamoto, Naohide Kinae: Intestinal absorption of luteolin and luteolin 7-O- [beta] -glucoside in rats and humans . In: FEBS Letters . 438, No. 3, 1998, pp. 220-4. doi : 10.1016 / S0014-5793 (98) 01304-0 . PMID 9827549 .
- ^ López-Lázaro M .: Distribution and biological activities of the flavonoid luteolin . In: Mini-Rev Med Chem . 9, No. 1, 2009, pp. 31-59. doi : 10.2174 / 138955709787001712 . PMID 19149659 .
- ↑ Kim TH, Custodio RJ, Cheong JH, Kim HJ, Jung YS: Sleep Promoting Effect of Luteolin in Mice via Adenosine A1 and A2A Receptors . In: Biomol Ther (Seoul) . tape 27 , 2019, p. 584-590 , doi : 10.4062 / biomolther.2019.149 , PMID 31646844 .
- ↑ Zhao G, Qin GW, Wang J, Chu WJ, Guo LH: Functional activation of monoamine transporters by luteolin and apigenin isolated from the fruit of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt . In: Neurochem. Int. . 56, No. 1, 2010, pp. 168-76. doi : 10.1016 / j.neuint.2009.09.015 . PMID 19815045 .
- ↑ De Martino L, Mencherini T, Mancini E, Aquino RP, De Almeida LF, De Feo V: In vitro phytotoxicity and antioxidant activity of selected flavonoids . In: Int J Mol Sci . 13, No. 5, 2012, pp. 5406-19. doi : 10.3390 / ijms13055406 . PMID 22754304 . PMC 3382788 (free full text).
- ↑ G. Seelinger, I. Merfort, CM Schempp: Anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic activities of luteolin. In: Planta Medica . Volume 74, Number 14, November 2008, pp. 1667-1677, doi : 10.1055 / s-0028-1088314 . PMID 18937165 .
- ↑ JM Pauff, R. Hille: Inhibition studies of bovine xanthine oxidase by luteolin, silibinin, quercetin, and curcumin. In: Journal of natural products. Volume 72, number 4, April 2009, pp. 725-731, doi : 10.1021 / np8007123 , PMID 19388706 , PMC 2673521 (free full text).

