Xanthine oxidase
| Xanthine oxidase | ||
|---|---|---|

|
||
| Ribbon model of the bovine xanthine oxidase monomer , pdb 1FIQ . Bound cofactors, FAD (red), FeS cluster (orange), molybdenum cofactor with molybdenum (yellow) and the bound inhibitor salicylate (blue) are highlighted. | ||
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 146 kDa / 1332 amino acids | |
| Secondary to quaternary structure | Homodimer | |
| Cofactor | 2 (2Fe-2S), FAD , molybdopterin | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene names | XDH ; XO; XS; XDHA | |
| External IDs | ||
| Enzyme classification | ||
| EC, category | 1.17.3.2 , oxidoreductase | |
| Response type | Hydroxylation | |
| Substrate | Xanthine + H 2 O + O 2 | |
| Products | Uric acid + H 2 O 2 | |
| Occurrence | ||
| Homology family | Xanthine dehydrogenase | |
| Parent taxon | Creature | |
| Orthologue | ||
| human | House mouse | |
| Entrez | 7498 | 22436 |
| Ensemble | ENSG00000158125 | ENSMUSG00000024066 |
| UniProt | P47989 | Q00519 |
| Refseq (mRNA) | NM_000379 | NM_011723 |
| Refseq (protein) | NP_000370 | NP_035853 |
| Gene locus | Chr 2: 31.33 - 31.41 Mb | Chr 17: 73.88 - 73.95 Mb |
| PubMed search | 7498 |
22436
|
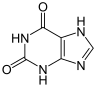
The xanthine oxidase (XO, sometimes XAO) or xanthine dehydrogenase (XDH) is a metalloenzyme (a hydroxylase which the) oxidation of hypoxanthine and xanthine to uric acid in the kidney and liver catalyzed.
Oxidation of hypoxanthine to xanthine:
Oxidation of xanthine to uric acid:
The active center contains a molybdenum atom bound in the form of the molybdenum cofactor (MoCo). Each subunit also contains two distinguishable two-iron-two-sulfur clusters (2Fe-2S) and one FAD molecule. In prokaryotes, the MoCo, (2Fe-2S) and FAD domains are encoded by two or three genes , respectively , in eukaryotes the domains are fused in one gene. The enzyme therefore occurs as a homodimer in eukaryotes and as a heterotetramer or heterohexamer in prokaryotes .
Elevated uric acid levels is known as gout . Gout can therefore also be treated with an inhibitor of xanthine oxidase; for example allopurinol or febuxostat . Allopurinol binds tightly to the reduced form of xanthine oxidase and thus inactivates it. This reduces the production of the sparingly soluble uric acid and increases the concentration of the more soluble compounds xanthine and hypoxanthine .
literature
- LG Nagler and LS Vartanyan: Subunit structure of bovine milk xanthine oxidase. Effect of limited cleavage by proteolytic enzymes on activity and structure. Biochim Biophys Acta . 427/1/ 1976 : 78-90- PMID 1260010
- JJ Truglio et al .: Crystal structures of the active and alloxanthine-inhibited forms of xanthine dehydrogenase from Rhodobacter capsulatus. Structure. 10/1/ 2002 : 115-25. PMID 11796116
- ST Smith et al .: Purification and properties of xanthine dehydroganase from Micrococcus lactilyticus. J Biol Chem . 242/18/ 1976 : 4108-4117. PMID 6061702