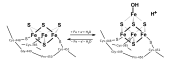Iron-sulfur clusters
Iron-sulfur clusters ( Fe-S centers ) are multiple complexes of iron and sulfur the size of clusters that are involved as cofactors in enzyme reactions. The most common and stable are (4Fe-4S) and (2Fe-2S). In general, clusters are destroyed when they are accessible to free oxygen. Accessibility depends on the protection of the binding enzyme.
These Fe-S centers act as electron transfer reactants , Lewis acids and radical generators in enzymes . For example, nitrogen can be converted into ammonia , hydrogen into protons and carbon monoxide into carbon dioxide :
The iron atoms of the centers are coordinated by inorganic sulfide and the side chains of amino acids . For example, cysteines can coordinate via their thiol group (see Fig.).
biosynthesis
Even under reducing, aqueous conditions, rhombic (2Fe-2S) complexes form spontaneously . Other metal ions, e.g. B. nickel or molybdenum can be included in the complex in a row. This happens particularly effectively in the organism with the participation of a protein complex that contains the iron-sulfur cluster framework protein (ISCU).
ISCU takes on the role of binding the iron atoms that are transported by ISCA, while the enzyme cysteine desulfurase provides sulfur atoms with cysteine consumption . First, (2Fe-2S) is put together, which eventually becomes (4Fe-4S) through dimerization. This process can take place in the mitochondria as well as in the cytosol, after which the finished (4Fe-4S) is transported into the plasma or incorporated into ready-made enzymes.
Occurrence
Anaerobic live bacteria and archaea partially also contain oxygen-sensitive enzymes with a nickel-, iron- and sulfur-containing center that the cluster C is referred to.
The enzyme nitrogenase contains an Fe-Mo-S cluster as a cofactor.
Iron-sulfur clusters are found in mitochondria, mitosomes, and hydrogenosomes.
List of human proteins with (2Fe-2S)
- NADH dehydrogenase , succinate dehydrogenase and cytochrome c reductase (complex I, II and III of the respiratory chain , citric acid cycle )
- Adrenodoxin (synthesis of thyroid hormones )
- Xanthine oxidase ( nucleotide metabolism )
- Aldehyde oxidase ( biotransformation , breakdown of nicotine )
- Ferrochelatase ( porphyrin metabolism )
- Miner1 and Miner2
List of human proteins with (4Fe-4S)
- NADH dehydrogenase and succinate dehydrogenase (complex I and II of the respiratory chain, citric acid cycle)
- Aconitase (citric acid cycle)
- Amidophosphoribosyltransferase ( purine metabolism , inosine monophosphate - de novo synthesis )
- Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (amino acid synthesis, synthesis of β- alanine )
- IREBP2 (iron metabolism)
- Lipoyl synthase (protein modification)
- the core enzymes DNA primase and endonuclease III-like
See also
literature
- H. Dobbek: How biological Fe-S centers activate CO2 . In: News from chemistry . tape 56 , no. 7–8 , 2008, pp. 734-737 , doi : 10.1002 / nadc.200857949 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Beinert H: Iron-sulfur proteins: ancient structures, still full of surprises . In: J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. . 5, No. 1, February 2000, pp. 2-15. doi : 10.1007 / s007750050002 . PMID 10766431 .
- ↑ Rouault TA, Tong WH: Iron-sulfur cluster biogenesis and human disease . In: Trends Genet. . 24, No. 8, August 2008, pp. 398-407. doi : 10.1016 / j.tig.2008.05.008 . PMID 18606475 . PMC 2574672 (free full text).
- ↑ Chandramouli K, Unciuleac MC, Naik S, Dean DR, Huynh BH, Johnson MK: Formation and properties of [4Fe-4S] clusters on the IscU scaffold protein . In: Biochemistry . 46, No. 23, June 2007, pp. 6804-11. doi : 10.1021 / bi6026659 . PMID 17506525 .
- ↑ Yang J, Bitoun JP, Ding H: Interplay of IscA and IscU in biogenesis of iron-sulfur clusters . In: J. Biol. Chem. . 281, No. 38, September 2006, pp. 27956-63. doi : 10.1074 / jbc.M601356200 . PMID 16877383 .