Amidophosphoribosyl transferase
| Amidophosphoribosyl transferase | ||
|---|---|---|

|
||
| Ribbon model of the PPAT tetramer from E. coli , according to PDB 1ECB | ||
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 506 amino acids | |
| Secondary to quaternary structure | Homodimer, -tetramer | |
| Cofactor | Mg 2+ , (4Fe-4S) | |
| Precursor | (517 aa) | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene name | PPAT | |
| External IDs | ||
| Enzyme classification | ||
| EC, category | 2.4.2.14 , transferase | |
| Response type | Transfer of a ribose residue | |
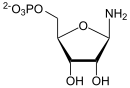
| Substrate | Glutamine + PRPP + H 2 O | |
| Products | Glutamic acid + PP i + 5-phosphoribosylamine | |
| Occurrence | ||
| Parent taxon | Creature | |
The amidophosphoribosyl transferase (ATase) , also called GPAT, is the enzyme that transfers a ribose residue from PRPP to glutamine . This reaction step in the purine biosynthesis of all living beings is definitive, that is, from the products of this and the next reactions, only IMP can be produced from now on . The ATase is localized in the cytosol , occurs in all tissue types and requires magnesium and an iron-sulfur cluster as cofactors .
Catalyzed reaction
5-phosphoribosylamine (PRA) and glutamate are formed from PRPP and glutamine. The reaction in equilibrium is shifted strongly to the right by hydrolysis of the diphosphate. IMP , GMP and AMP act as inhibitors .
Individual evidence
- ↑ UniProt Q06203
- ↑ Jassal / reactome: 5-phospho-alpha-D-ribose 1-diphosphate (PRPP) + H2O + L-glutamine ⇔ 5-phosphoribosylamine + L-glutamate + pyrophosphate ( Memento of the original from May 13, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info : The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
Web links
Wikibooks: Purine Metabolism - Learning and Teaching Materials