Adenosine monophosphate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
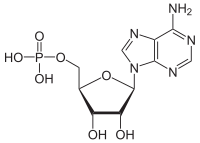
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Adenosine monophosphate | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 10 H 14 N 5 O 7 P | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless, finely crystalline, odorless powder |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 347.2 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
196-200 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in water |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Adenosine monophosphate ( AMP ), also known as adenylate , is a chemical compound that occurs in the metabolism of all living things. It is a nucleotide , the phosphoric acid ester of the nucleoside adenosine . AMP, together with cytidine monophosphate ( CMP ), guanosine monophosphate ( GMP ) and uridine monophosphate ( UMP ), form the basic building blocks of ribonucleic acid ( RNA ). In the past, AMP was assigned to the B vitamins and sometimes referred to as "vitamin B8".
Natural occurrence and meaning
As a component of RNA , AMP occurs in all living things. The RNA is used in cells to convert genetic information from deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA ) into proteins .
AMP is the breakdown product of cAMP , ADP and ATP and at the same time their starting material. The phosphate group at the 5'-end of the ribose cannot be used in the cell for the phosphorylation of other groups, since the group transfer potential is too low (phosphate does not have enough energy to react).
Use as a bitter blocker
AMP was the first substance that was discovered to block the tongue's bitter sensation. AMP blocks the G-protein gustducin , which is involved in bitter perception. Attempts are made to make foods and medicines more palatable with bitter blockers.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on adenosine 5′-monophosphate. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed December 10, 2014.
- ↑ a b Data sheet Adenosine 5′-monophosphate from Acros, accessed on February 19, 2018.
- ↑ "Vitamin B8" on vitamine.com
- ↑ Bitter blocker backed by FDA , September 19, 2004, accessed April 29, 2018.