Xanthine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Xanthine | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 5 H 4 N 4 O 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless solid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 152.11 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
350 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
very little water soluble (69 mg l −1 at 16 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Xanthine is a naturally occurring substance of the nucleotide metabolism . It is an intermediate product in the breakdown of purines and is converted into uric acid by xanthine oxidase . In addition, xanthine is the lead substance of the group of xanthines, which includes the purine alkaloids caffeine , theobromine and theophylline from tea leaves , coffee beans , cocoa , cola nuts , mate and guarana .
Occurrence
Xanthine is an intermediate product of purine degradation by hydroxylation at positions 2 and 6; the resulting Dilactim tautomerizes completely to Di lactam . It arises z. B. in wine in small quantities through the self-digestion of yeasts . It is also found in coffee beans, potatoes , tea leaves and mate, the Argentine national drink. There it is said to have a stimulating effect due to its special structure. In the human body, some organs such as the blood, muscles and liver contain xanthine, which is also excreted in the urine .
properties
Xanthine is a colorless, crystalline solid that dissolves well in ethyl acetate , acids and bases, very little (69 mg · l −1 ) in water at 16 ° C and only moderately in hot water and ethanol .
The nucleoside xanthosine and the nucleotide xanthosine monophosphate are derived from xanthine .
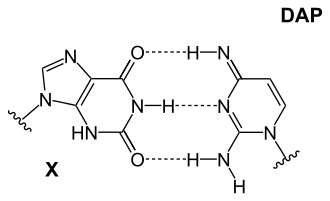
It is used together with 2,4-diaminopyrimidine to investigate unusual base pairings in DNA .
Pathophysiology
Xanthine stones are relatively rare. They can occur with xanthinuria . The cause of the not so rare xanthinuria is a genetic defect in xanthine oxidase. Since xanthine is medically relatively soluble in water , only about 40% of those affected develop urinary stones . Xanthinuria can also occur with treatment with allopurinol . Allopurinol inhibits xanthine oxidase and as a medicament for lowering serum uric acid levels (especially when gout - patients ) were used. If the fluid intake is too low, a xanthine concentration that is critical for stone formation can be reached in the urine .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on XANTHINE in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on March 29, 2020.
- ↑ a b c d Entry on xanthine. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on May 24, 2012.
- ↑ a b c Entry on xanthine in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ↑ a b Xanthine data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 25, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b Ammon, HPT: Hunnius Pharmaceutical Dictionary , Walter de Gruyter, 2004, ISBN 3-11-017487-1 , p. 1623.
- ↑ ST Madariaga, JG Contreras: "Tautomerism of xanthine and its pairing with 2,6-diaminopyrimidine: An ab initio study in the gas phase and aqueous solution", J. Chil. Chem. Soc. , 2003 , 48 (4), pp. 129-133 ( doi: 10.4067 / S0717-97072003000400021 ).
Web links
- Entry for xanthines in the Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) , accessed November 3, 2013.