Glutaraldehyde
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Glutaraldehyde | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 5 H 8 O 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless, pungent smelling liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 100.12 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.05 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−14 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
187–189 ° C (decomposition) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
2.3 k Pa (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
miscible with water |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
DFG / Switzerland: 0.05 ml m −3 or 0.21 mg m −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
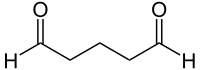
Glutaraldehyde , systematically referred to as 1,5-pentanedial , is a colorless chemical compound that is liquid at room temperature and has a sharp, unpleasant odor. It consists of a chain of five carbon atoms with a total of eight hydrogen atoms . There are aldehyde functions at both ends . So glutaraldehyde is the dialdehyde of n -pentane . Due to its high reactivity, it is not commercially available as a pure substance, but only in the form of mostly aqueous solutions .
use
Glutaraldehyde appears as an intermediate in the industrial manufacturing process of some chemicals and is used directly:
- to medical and dental to equipment disinfected .
- in water treatment for industrial purposes, e.g. hydraulic fracturing
- as a disinfectant for industrial plants, e.g. B. Pipelines or production facilities in the cosmetic industry
- as an additive in cleaning agents
- as a chemical preservative
- as a tanning agent for leather
- as an embalming fluid ( fixative ) for tissue in light microscopy and electron microscopy
- as a cross-linker when coating ELISA plates with peptides
- as a cross-linker between proteins . In the case of immobilization by cross-linking, an enzyme is covalently bound by the bifunctional glutaraldehyde, in that the two reactive aldehyde groups are each linked to a free amino group of the enzyme. The aim is to increase the biological half-life by increasing mechanical and thermal stability and reducing proteolysis .
- as a controversial plant fertilizer (carbon source) with a slight algicidal effect in the aquarium hobby
safety instructions
Glutaraldehyde is toxic and causes serious eye, nose, throat, and lung irritation, including headache , drowsiness, and dizziness .
Ecological relevance
Glutaraldehyde is particularly toxic to aquatic organisms.
Since the beginning of 2008, plans by the Nord Stream consortium led by the energy company Gazprom have brought it into public awareness. Consideration is being given to cleaning the newly built Baltic Sea pipeline using an aqueous glutaraldehyde solution of an undisclosed concentration. The 2.3 million cubic meters of solution required for this are then to be pumped into the Baltic Sea . A paper by the German Ministry of the Environment suggests that the fauna and flora of the Baltic Sea are already heavily polluted by pollutants.
Web links
- Entry on glutaraldehyde in the Consumer Product Information Database
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on glutaraldehyde. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on October 7, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on glutaraldehyde in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 8, 2018(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ baua.de: Rationale for Glutaral Occupational Exposure Limits in TRGS 900 , accessed on May 15, 2016.
- ↑ Entry on glutaral in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Data sheet Glutaraldehyde solution from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on February 1, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values (search for 111-30-8 or glutaraldehyde ), accessed on November 2, 2015.
- ↑ Pipeline: Gazprom wants to pump poison into the Baltic Sea. In: Spiegel Online . February 23, 2008, accessed December 19, 2019 .
- ↑ Answer of the Federal Government to the short question on the Baltic Sea pipeline (PDF; 80 kB) Cleaning of the planned Gazprom gas pipeline with glutaraldehyde.



