Bailey peptide synthesis
The Bailey peptide synthesis is a name reaction of organic chemistry developed in 1949 by JL Bailey . It is a method for peptide synthesis and describes the synthesis of a peptide based on the reaction of α- amino acid N- carboxylic acid anhydrides (NCAs or Leuchs' anhydrides ) with amino acids or peptide esters. The peculiarity of this name reaction is the short reaction time and the high yield of the peptide to be obtained.
Overview reaction
The reaction can be carried out at low temperatures in organic solvents. The radicals R 1 to R 2 are organic radicals or hydrogen atoms, R 3 corresponds to the residual body of an amino acid or a peptide ester, belonging to the amino group shown:
Reaction mechanism
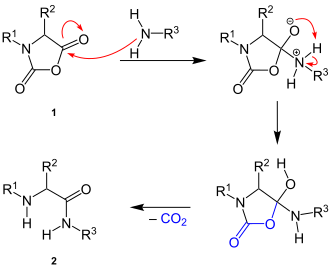
The exact mechanism of the reaction is not known. There is a nucleophilic attack of the amino group on the carbon atom of the anhydride group of the N- carboxylic acid anhydride ( 1 ). After an intramolecular proton migration, there is a 1,4-proton shift and the splitting off of carbon dioxide, which creates the peptide bond in the end product ( 2 ):
Atomic economy
The atom- economical advantage of using NCAs for peptide formation is that there is no need for a protective group to be present on the functional group for reaction with amino acids . For example, the Merrifield synthesis is based on the use of Boc and Bzl protective groups, which still have to be removed after the reaction. In the case of the Bailey peptide synthesis, the free peptide is present directly after the reaction. However, there is the possibility of undesirable by-products that are difficult to remove. An N -substitution of the NCA (for example by an o -Nitrophenylsulfenylrest) can facilitate the subsequent cleaning process, however, deteriorates conversely the atom economy of the reaction.
NCAs can be synthesized by means of the Leuchs reaction or by reacting N - ( benzyloxycarbonyl ) amino acids with oxalyl chloride . In the latter case, one would again have to speak of a less efficient process in terms of atomic economy.
Synthesized peptides
The following peptides were synthesized using this method until 1949:
- DL - Ala - Gly
- L - Tyr - Gly
- DL - Tyr - Tyr
- DL - Ala - DL - Ala - Gly
- DL -di- Ala - L - cystinyl -di- Gly
- DL - Ala - L - Tyr - Gly
- DL - Ala - L - Tyr - Gly - Gly
- DL - Ala - DL - Ala -L- Tyr - Gly - Gly
- L - Tyr - L - Tyr - L - Tyr
- L - Cystinyl di- Gly
Individual evidence
- ↑ JL Bailey: A new peptide synthesis. In: Nature. Volume 164, Number 4177, November 1949, p. 889, PMID 15407090 .
- ↑ a b c d e f Daniel Zerong Wang: Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents . tape 1 . John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken New Jersey 2009, ISBN 978-0-471-70450-8 , pp. 156-159 .
- ↑ a b J. Leggett Bailey: A new Peptide Synthesis. In: Nature . Volume 164, No. 4177, 1949, p. 889, DOI: 10.1038 / 164889a0 .
- ↑ a b c d Ryoichi Katakai: Peptide Synthesis Using o-Nitrophenylsulfenyl N-Carboxy α-Amino Acid Anhydrides. In: The Journal of Organic Chemistry. , Volume 40, No. 19, 1975, pp. 2697-2702, DOI: 10.1021 / jo00907a001 .
- ↑ Hans-Dieter Jakubke: Peptides. Chemistry and biology . Spektrum Akademischer Verlag GmbH, Heidelberg Berlin Oxford 1996, ISBN 3-8274-0000-7 , p. 178 .
- ↑ Hans Rytger Kricheldorf: α-Aminoacid-N-Carboxy-Anhydrides and Related Heterocycles. Syntheses, Properties, Peptide Synthesis, Polymerization. Springer Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, 1987, pp. 1-4, DOI: 10.1007 / 978-3-642-71586-0 , ISBN 978-3-642-71588-4 (print), ISBN 978-3-642-71586 -0 (online).
- ↑ D. Konopinska, IZ Siemion: Synthesis of N-Carboxy-α-amino Acid Anhydrides. In: Angewandte Chemie International Edition. Volume 6, No. 3, 1967, p. 248, DOI: 10.1002 / anie.196702481 .
literature
- P. Katsoyannis: The Chemistry of Polypeptides. Springer Science & Business Media, 2012, ISBN 978-1-461-34571-8 , p. 129.