Floor space (architecture)
The base area of a building is in the original sense that area with which a building touches the ground. It is in this sense be equated with the "built-up area" (as opposed to " over built area" which includes roof overhangs and canopies). The base area is measured at floor level on the finished wall surfaces, i.e. including wood paneling, thermal insulation and external plaster.
In a broader sense, the base area also refers to the areas that the upper storeys occupy at floor level. In principle, it is then comparable with the floor area of the building planning law .
The gross floor area (GFA) (according to the external dimensions of the building) is divided according to DIN 277 into the usable net room area (NRF) and the construction floor area (KGF) (walls, supports, etc.). The net room area, in turn, consists of the pure usable area (NUF) , the traffic area (VF) and the technical area (TF) (referred to as technical functional area (TF) until 2016 and as functional area (FF) before 2005 ).
The living space as a special form of usable area is determined according to the living space ordinance .
The individual areas are used to determine the costs of building construction and to compare buildings. The terms and calculation bases were defined in DIN 277 in the 1987 version, which was amended in 1993, 2005 and 2016. With the amendment from 2005, the terms main usable area (HNF) and secondary usable area (NNF) have been dropped. With the amendment from 2016, the term "net floor area (NGF)" was changed to "net room area (NRF)" and the "usable area (NF)" was renamed to "usable area (NUF)".
Gross floor area
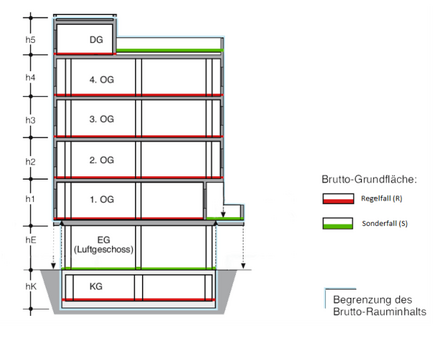
Gross floor area (GFA) refers to the area that is calculated from the sum of all floor areas of all floor plan levels of a building. It is to be determined by floor.
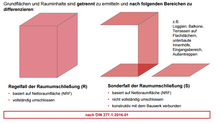
According to DIN 277, which was newly published in 2016, a distinction is only made between the normal case (R) and the special case (S) for determining the gross floor area.
- As a rule, all rooms and areas that are completely enclosed.
- The special case relates to rooms and areas that are structurally connected to the building, but are not completely enclosed, e.g. B .:
- Loggias
- Terraces on flat roofs
- Balconies
- sub-built courtyards
- Entrance areas
- Outside stairs
- The special areas themselves are measured at the points where they are not enclosed up to the limit of the vertical projection of their coverage. Construction areas (KGF) between R and S are to be assigned to area R.
Thus, in contrast to the floor area (GF) according to BauNVO , the GFA includes all floors of a building including attics that are not considered full floors and the underground areas (cellars, underground car parks, etc.). However, the base areas of unusable roof areas and structural cavities, e.g. B. in ventilated roofs or over suspended ceilings.
If the floor is partially missing on a floor to separate the floor from the floor below, as is the case, for example, when a very high floor is partially divided in height by an intermediate level designed as a gallery , then the air space on the upper floor is also not taken into account.
Very often the term gross floor area is mistakenly used instead of gross floor area , which is not used in any standard.
For calculations according to the standard of the valuation guideline with NHK 2010, uncovered areas and balconies are not included in the gross floor area. The outer dimensions of the components are at floor level , including their clothing such. B. plaster to apply.
Construction footprint
The construction base area (KGF) is the sum of the base areas of all rising components. This includes in particular the (unusable) standing areas of the walls. The finished dimensions of the components are to be set at floor level, including plaster and ceiling-high cladding. The KGF can also be determined as the difference between the GFA and the NRF.
Net room area
| 1 | Usable area (NUF) | Living and staying |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | Office work | |
| 3 | Production, manual and machine work, experiments |
|
| 4th | Store, distribute and sell | |
| 5 | Education, teaching and culture | |
| 6th | Healing and nurturing | |
| 7th | Other usable areas | |
| 8th | Technical area (TF) | Technical equipment |
| 9 | Traffic area (VF) | Traffic development and security |
The net room area (NRF) is the sum of the usable floor space of a building. To calculate it, it is subdivided into usage groups according to the table below:
- the use surface (NUF) as appropriate for proper use of a building effectively usable floor space.
- the technical area (TF) , which is used to accommodate central building services systems (e.g. heating, machine room for the elevator, room for operating air conditioning).
- the traffic area (VF) , which is used for access to the rooms, for traffic within buildings or for leaving in an emergency.
Norms
See also
- The building usable area is a term from the German Energy Saving Ordinance and is determined by a rough calculation method based on the heated building volume and floor height and serves as the energy reference area size for residential buildings.
literature
- Dietrich-Alexander Möller: Planning and building economics Volume 1: Basics of economic building planning. R. Oldenbourg Verlag, Munich / Vienna, ISBN 3-486-58171-6 .
- Wolfgang Feist: Energy reference area. Passive House Institute May 19, 2007. (online)