Bucherer reaction
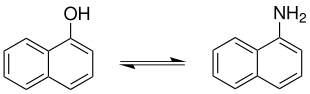
The Bucherer reaction is an organic-chemical name reaction and named after Hans Theodor Bucherer (1869–1949). The reaction is also called the Bucherer-Lepetit reaction or, incorrectly, the Bucherer-Le-Petit reaction. It describes the reaction of naphthols to naphthylamines in the presence of ammonia and sodium hydrogen sulfite . 1-naphthylamine is formed from 1-naphthol :
The positionally isomeric 2-naphthylamine
is obtained analogously from 2-naphthol :
The French chemist Robert Lepetit was the first to discover this reaction in 1898, but Bucherer, independently of Lepetit, determined its reversibility and enormous possibilities for the chemical industry. Bucherer published his results in 1904, which means that his name is firmly linked to the reaction.
The Bucherer reaction takes place in an aqueous medium under catalysis by sulfite . This reversibly attacks the protonated aromatic, tautomerizes to hydrogen sulfite and is attacked by ammonia or an amine . After splitting off the sulfite, the corresponding naphthylamine is formed, in which the hydroxyl group of the naphthol is formally substituted by an amino group .
Reaction mechanism
The reaction is described here using 1-naphthol as an example and proceeds according to an addition-elimination mechanism . In the first step, a proton is attached to the carbon atom with the highest electron density, i.e. preferably to C2 or C4, of the 1-naphthol ( 1 ). This leads to the resonance-stabilized adduct 2 . In the next step, the hydrogen sulfite anion attaches to the C3 carbon. A tautomerization to the energetically more favorable molecule 3 follows . This is nucleophilically attacked by the amine, in this case ammonia. The resonance-stabilized cation 4 is formed with the elimination of water . Deprotonation provides the enamine 5 . The enamine eliminates the hydrogen sulfite with formation of 1-naphthylamine ( 6 ).
The reaction is reversible and can be summarized as follows:
application
The Bucherer reaction is a key reaction in the synthesis of carbazoles . 2-Napthol or 2-Napthylamine reacts with phenylhydrazine with the addition of sodium hydrogen sulfite to form a carbazole:
Individual evidence
- ↑ Hans Th. Bucherer: On the action of sulfuric acid salts on aromatic amido and hydroxyl compounds. In: Journal for Practical Chemistry. 69, No. 1, 1904, pp. 49-91, doi : 10.1002 / prac.19040690105 .
- ↑ H. Seeboth: The Bucherer Reaction and the Preparative Use of its Intermediate Products. In: Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English. 6, No. 4, 1967, pp. 307-317, doi : 10.1002 / anie.196703071 (mechanism).
- ^ R. Adams et al .: Organic Reactions Vol I. Wiley, 1942.
- ↑ Winfried R. Pötsch u. a .: Lexicon of important chemists . Bibliographisches Institut, Leipzig 1989, ISBN 978-3-323-00185-5 , pp. 71-72.
- ↑ MB Smith, J. March: Advanced Organic Chemistry . Wiley, 2001, ISBN 0-471-58589-0 .
- ↑ Ivan Ernest: Binding, Structure and Reaction Mechanisms in Organic Chemistry . Springer, 1972, ISBN 3-211-81060-9 , pp. 244-245.
- ↑ Hans Th. Bucherer, André Grolée, (1906) About nitriles arylated glycines. Ber. German Chem. Ges., 39: 986-1013, doi : 10.1002 / cber.190603901154 .
- ^ Z. Wang: Comprehensive organic name reactions and reagents Volume 1 . John Wiley, Hoboken (NJ) 2009, ISBN 978-0-470-28662-3 , pp. 549 .