Enamines
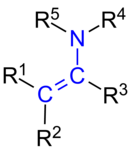
Enamines are unsaturated chemical compounds that result from the reaction of aldehydes or ketones with secondary amines (e.g. pyrrolidine , piperidine or morpholine ) with elimination of water (H 2 O). With primary amines or ammonia as starting materials, the tautomer equilibrium is not on the side of the enamine, but on the side of the imine (see keto-enol tautomerism ). They have the basic form R 1 R 2 C = CR 3 -NR 4 R 5 , where R x each stands for a radical .
The term “enamine” is derived from the prefix “en” (as a designation for the alkene contained , similar to “enol”) and “ amine ”, which is attached to the alkene as a functional group .
If one of the radicals R 4 or R 5 on the nitrogen is a hydrogen atom , then the enamine is a tautomeric form of the corresponding imine . Then the two forms face each other in an equilibrium reaction ( enamine-imine tautomerism ). A similar reaction is the keto-enol tautomerism . In both reactions, the hydrogen atom swaps its place between the heteroatom (oxygen or nitrogen) and the second carbon atom:
The simplest enamine (all residues consist of hydrogen atoms) is vinylamine .
use
Enamines are important in the synthesis of chemical compounds, since the spreading of the charge in the mesomeric system allows electrophiles (e.g. acid chlorides and activated alkylating agents such as allyl halides and α-halocarboxylic acid esters and electron-poor alkenes) to react easily at the second carbon atom.
Notice also
- Enamine alkylation and acylation
- Thorpe-Ziegler reaction
- Stork enamine reaction
- Enamine-lactone rearrangement
- Michael addition (can be done with enamines)
- Nucleophilic addition
Individual evidence
- ↑ Eberhard Breitmaier, Günther Jung: Organische Chemie , 7th edition, Thieme Verlag, 2012, p. 325, ISBN 978-3-13-541507-9 .
- ↑ Ludwig Gattermann and Heinrich Wieland : The practice of the organic chemist , ISBN 3-11-006654-8 .
- ↑ namesreaktionen.de: Enamine alkylation and acylation