Nuclear Test Ban Treaty
The contract for the Comprehensive Nuclear Test-Ban , also Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty ( English Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty , CTBT ) is a not yet entered into force international treaty that all nuclear tests should prohibit.
content
The Nuclear Test Ban Treaty prohibits the implementation of any type of nuclear weapon explosion , whether for civil or military purposes. Aid to this is also prohibited. This goes beyond the 1963 Treaty on the Ban on Nuclear Weapons Tests in the Atmosphere, Space and Underwater .
To ensure compliance with the treaty, it includes the establishment of the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Organization (CTBTO). It is tasked with setting up a surveillance system that can register nuclear weapon explosions worldwide. This monitoring system consists of a network of globally distributed stations to monitor earthquakes , radionuclides , underwater sound and infrasound that their measurements to the International Data Center in Vienna transmit. In addition, registered on-site inspections are planned.
The treaty comes into force 180 days after the states named in Annex 2 of the treaty have ratified the treaty . These 44 states are those which, according to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), had nuclear technology in 1995 , including the official nuclear powers .
The validity of the contract is unlimited.
history
The nuclear test ban treaty was drawn up by the UN Disarmament Conference and adopted on September 10, 1996 with 158 votes out of 173 by the UN General Assembly . Since then, it has been available to the international community for signature and ratification .
On 19 November 1996, was Preparatory Commission ( Preparatory Commission , shortly PrepCom ) was established as a forerunner of the CTBTO. It is tasked with preparing the entry into force of the contract and in particular setting up the international monitoring system. By February 2017, 284 of the 337 planned measuring stations were certified and fully functional.
State of ratification
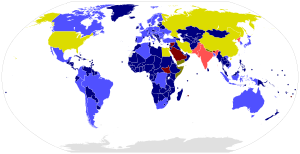
So far (as of February 2017) 183 states have signed the treaty and 166 ratified it. The last states to ratify the treaty were Myanmar and Swaziland on September 21, 2016.
Of the 44 nuclear technology states, 41 have signed and 36 ratified. For the treaty to come into force, the following states still have to ratify it: Egypt , the People's Republic of China , India , Iran , Israel , North Korea , Pakistan and the USA (ratification rejected by the Senate on October 13, 1999 ).
Of these states, India, Pakistan and North Korea have not even signed the treaty.
Germany and Austria ratified the agreement in 1998, Switzerland in 1999.
See also
Web links
- English contract text
- German translation (PDF; 401 KiB)
- atomwaffena-z.info: test stop
Individual evidence
- ↑ CTBTO World Map - International Monitoring System. CTBTO Preparatory Commission, accessed February 10, 2017 .
- ^ List of signatory states (accessed February 10, 2017).