Calicheamicins
Calicheamicins are a group of structurally very closely related, highly toxic cell toxins . They are 1000 times more potent than adriamycin . These bacterial toxins are produced by the bacterium Micromonospora echinospora . Ingestion of a few grams inevitably leads to death, antidotes are not known. In a correspondingly diluted form, the substance is used in targeted cancer therapy .
properties
The family of calicheamicins includes various structurally closely related chemical compounds. They are structurally, to their biological effect and its mechanism of action esperamicins very similar and also included alongside the enediyne a Allyltrisulfideinheit and seated at the bridgehead enone functionality . Their structures were developed by LEE et al. Published in 1987 and corrected in 1989. The best-known representative is calicheamicin γ1 I , which can now also be produced synthetically.
| Examples of calicheamicins | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name (s) |
Endyne - substructure |
R = |
CAS - number |
PubChem | Molecular formula | Molar mass |
|||
|

|

|
44307061 | C 48 H 62 IN 3 O 17 S 4 | 1208.18 g mol −1 | ||||
|

|
44307057 | C 56 H 76 BrN 3 O 21 S 4 | 1335.37 g mol −1 | |||||
|

|
44307331 | C 55 H 74 BrN 3 O 21 S 4 | 1321.35 g mol −1 | |||||
|

|
44307145 | C 54 H 72 IN 3 O 21 S 4 | 1354.32 g mol −1 | |||||
|

|
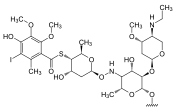
|
103716-12-7 | 6450514 | C 48 H 62 IN 3 O 17 S 4 | 1208.18 g mol −1 | |||
|

|
103716-13-8 | 6450515 | C 47 H 59 IN 2 O 19 S 4 | 1211.14 g mol −1 | ||||
|

|

|
108212-75-5 | 6438329 | C 56 H 78 IN 3 O 21 S 4 | 1384.39 g mol −1 | |||
|

|
142518-72-7 | 6449957 | C 32 H 43 N 3 O 11 S 3 | 741.89 g mol −1 | ||||
|

|
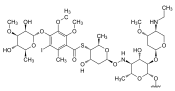
|
10486648 | C 55 H 74 IN 3 O 21 S 4 | 1368.35 g mol −1 | ||||
|
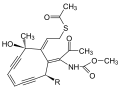
|

|
44403705 | C 57 H 78 IN 3 O 22 S 2 | 1348.27 g mol −1 | ||||
|
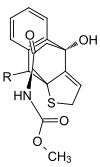
|

|
128050-91-9 | 5488030 | C 54 H 74 IN 3 O 21 S 2 | 1292.21 g mol −1 | |||
effect
Calicheamicins carry an enediyne structural unit that is known to enter into Bergman cyclizations and the resulting diradicals lead to a double-strand break in the DNA . Such a mechanism of action is also being discussed for the calicheamicins.
mythology
The Greek poet Hesiod describes: According to legend, the gods who violated the laws of Olympus had to drink the water of the Styx from a golden goblet . It is believed that the rocks under the Mavronero River , which was associated with Styx, were densely populated with Micromonospora echinospora , so that the amount of dissolved calicheamicin from one cup was sufficient to be fatal.
history
Allegedly Alexander the Great was killed by a goblet of Styx water. The historians say that he suffered severe pain and an insatiable thirst before he died after a week. This is consistent with the symptoms of calicheamicin poisoning. The Greek historian Pausanias writes that goats who accidentally drank the water of the Styx fell dead a short time later for no apparent reason.
Individual evidence
- ^ Theodor Dingermann: Pharmaceutical Biology. Springer, 2002, ISBN 978-3-540-42844-2 , p. 231 ( limited preview in Google book search).
- ↑ Nicolaou KC, Chen JS, Dalby SM: From nature to the laboratory and into the clinic . In: Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry . 17, No. 6, March 2009, pp. 2290-2303. PMID 19028103 . PMC 2665039 (free full text).
- ^ MD Lee, JK Manning, DR Williams, NA Kuck, RT Testa, DB Borders: Calicheamicins, a novel family of antitumor antibiotics. 3. Isolation, purification and characterization of calicheamicins beta 1Br, gamma 1Br, alpha 2I, alpha 3I, beta 1I, gamma 1I and delta 1I. In: The Journal of antibiotics . Volume 42, Number 7, July 1989, pp. 1070-1087, PMID 2753814 .
- ↑ Folkert Boße: Studies on the Synthesis of New Dynemicin Analogues (PDF; 737 kB)
- ↑ S. Walker; R. Landovitz; WD thing; GA Ellestad; D. Kahne: Cleavage behavior of calicheamicin γ1 and calicheamicin T . In: Proc Natl Acad Sci USA . 89, No. 10, 1992, pp. 4608-4612. doi : 10.1073 / pnas.89.10.4608 . PMID 1584797 . PMC 49132 (free full text).
- ↑ Angelika Franz: Archeology: Week of torments. In: Spiegel Online . August 2, 2010, accessed July 29, 2016 .
- ↑ Alexander the Great poisoned by the River Styx . August 4, 2010. Retrieved August 8, 2010.