Claisen rearrangement
The Claisen rearrangement is a reaction from the field of organic chemistry and named after the German chemist Ludwig Claisen (1851–1930). It represents a [3,3] - Sigmatropic rearrangement of allyl - vinyl ethers to γ, δ-unsaturated carbonyl compounds is Another name for the reaction is oxa. Cope rearrangement . Various textbooks contain various statements as to whether phenyl or vinyl allyl ethers were examined first. The Claisen rearrangement is an example of valence isomerization .
meaning
The reaction is valuable for the synthetic chemist; together with the simultaneous extension of the carbon chain, the carbonyl compounds of interest for further syntheses are obtained. In addition, starting from enantiomerically pure starting materials, products with a high enantiomeric excess are obtained .
mechanism
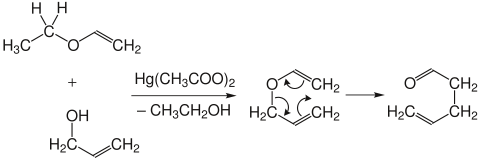
The Claisen rearrangement is in principle reversible, but the equilibrium is on the product side because of the greater thermodynamic stability of the carbonyl compounds. The allyl vinyl ethers are produced by the mercury or acid- catalyzed reaction of the ethyl vinyl ethers with allyl alcohol . Since the allyl vinyl ethers partially rearrange during the synthesis, they are usually not isolated.
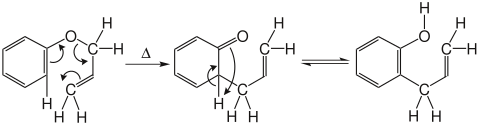
If allylphenyl ether is heated to 200 ° C., the ketone to be expected is formed first according to the mechanism below , which then rearranges into the corresponding ortho- allylphenol with rearomatization and proton transfer analogous to keto-enol tautomerism .
Investigations using the kinetic isotope effect showed that the OC α bond is already 50 to 60% broken, while the C ortho -C γ bond is only 10 to 20% formed. This means that the Claisen rearrangement is a concerted but asynchronous rearrangement.
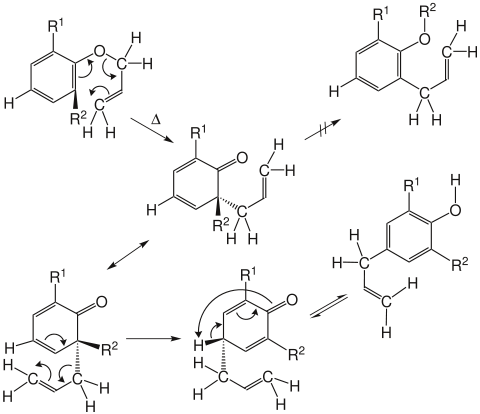
If the two ortho - positions occupied by substituents, [3,3] sigmatropic rearrangement is done by a second (in this case, a Cope rearrangement ) formation of the corresponding para -Produktes .
variants
Because of these advantages, numerous variants have been developed. Five more well-known variants of the Claisen rearrangement are shown below.
Johnson variant
In the orthoester or Johnson variant , a carboxylic acid orthoester is reacted with the allyl alcohol under acid catalysis. Two molecules of methanol are split off one after the other. This is followed by the rearrangement to form the unsaturated ester .
Eschenmoser variant
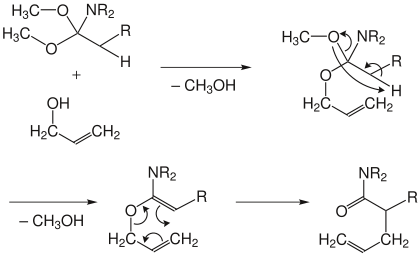
In the Eschenmoser variant, a dimethyl acetal of a carboxamide is used. This reacts with the allyl alcohol, splitting off a molecule of methanol and forming a mixed acetal. The acetal eliminates another molecule of methanol. Then the rearrangement to an unsaturated amide takes place .
Carroll variant
In the Carroll variant, the allyl alcohol is first reacted with diketene . This primarily produces a β- keto acid , which decarboxylates to the unsaturated ketone .
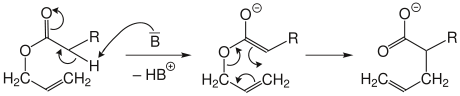
Arnold variant
In the Arnold variant, an allyl ester is deprotonated by strong bases (B). The resulting ester enolate then rearranges to form the salt of the unsaturated carboxylic acid.
Ireland variant
In the Ireland variant, also known as the ester enolate Claisen rearrangement, the allyl ester is first deprotonated, as is the case with the Arnold variant. But then the trimethylsilyl ether of the ester enolate is produced. This rearranges under particularly mild conditions. The silyl ester can be split particularly gently.
literature
- L. Claisen: On rearrangement of phenol-allyl ethers into C-allyl-phenols. In: Reports of the German Chemical Society. 45, No. 3, 1912, pp. 3157-3166, doi : 10.1002 / cber.19120450348 .
- FA Carey, RJ Sundberg, Organic Chemistry . VCH 1995, ISBN 3-527-29217-9 , p. 1063 ff.
- Hans Beyer , Wolfgang Walter : Textbook of organic chemistry . 23. revised and updated edition, S. Hirzel Verlag, Stuttgart / Leipzig 1998, ISBN 3-7776-0808-4 .
Web links
- Learning unit at ChemgaPedia
- Diederich, Michel: Development and investigation of the zwitterionic aza-Claisen rearrangement for the synthesis of optically active nine-membered lactams. Asymmetric total synthesis of the indolizidine alkaloid (-) - 8a-epi-dendroprimin. Dissertation, FU Berlin 2000. urn : nbn: de: kobv: 188-2000000897