Cobalt (II) thiocyanate
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Surname | Cobalt (II) thiocyanate | |||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||
| Ratio formula | Co (SCN) 2 | |||||||||
| Brief description |
yellow-brown solid |
|||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | 175.10 g mol −1 | |||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||
| density |
1.786 g cm −3 (trihydrate) |
|||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||
Cobalt (II) thiocyanate is an inorganic chemical compound of cobalt from the group of thiocyanates .
Extraction and presentation
Cobalt (II) thiocyanate can be obtained by reacting cobalt (II) sulfate with barium thiocyanate .
It is also possible to produce it by reacting thiocyanic acid with cobalt (II) carbonate or by reacting ammonium thiocyanate and cobalt salts in neutral solution.
properties
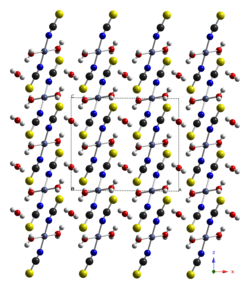
Cobalt (II) thiocyanate is a yellow-brown solid that is soluble in water. The solution is reddish in color. The trihydrate has a purple to brown color that looks red in transmitted light and dissolves in water to turn blue. It converts to anhydrate from 105 ° C. The trihydrate has a monoclinic crystal structure with the space group C 2 / c (space group no. 15) .
use
Cobalt (II) thiocyanate can be used to detect alkaloids , methadone , ephedrine , cocaine and other drugs. If these are added to a 2 percent solution of cobalt (II) thiocyanate, a blue or blue-green precipitate forms, depending on the compound. This is called the Scott test (with the addition of chloroform ). The trihydrate is used as a humidity indicator. An aqueous solution of the compound can be used to determine nonionic surfactants based on ethoxylates in water.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Dale L. Perry: Handbook of Inorganic Compounds . CRC Press, 1995, ISBN 978-0-8493-8671-8 , pp. 131 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b c data sheet cobalt (II) thiocyanate, 99.9% trace metals basis from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on December 10, 2015 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c F. H. Cano, S. García-Blanco, AG Laverat: The crystal structure of cobalt (II) thiocyanate trihydrate. In: Acta Crystallographica Section B Structural Crystallography and Crystal Chemistry. 32, p. 1526, doi : 10.1107 / S0567740876005694 .
- ^ William M. Haynes: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 96th Edition . CRC Press, 2015, ISBN 978-1-4822-6097-7 , pp. 60 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ Philipp Kurz, Norbert Stock: Synthetic Inorganic Chemistry Basic Course . Walter de Gruyter, 2013, ISBN 978-3-11-025875-2 , p. 73 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ Helmut Hofmann, Gerhart Jander: Qualitative analysis . Walter de Gruyter, 1972, ISBN 978-3-11-003653-4 , p. 123 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ David E. Newton: Forensic Chemistry . Infobase Publishing, 2007, ISBN 978-1-4381-0976-3 , pp. 86 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Rick Houghton: Field Confirmation Testing for Suspicious Substances . CRC Press, 2009, ISBN 978-1-4200-8616-4 , pp. 174 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Rolf Pohling: Chemical reactions in water analysis . Springer-Verlag, 2015, ISBN 978-3-642-36354-2 , pp. 344 ( limited preview in Google Book search).



