Cycasin
| Structural formula | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
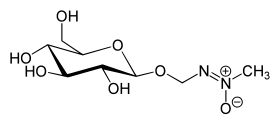
|
||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Surname | Cycasin | |||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 16 N 2 O 7 | |||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | 252.22 g mol −1 | |||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||
| Melting point |
154 ° C |
|||||||||
| solubility |
water soluble |
|||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||
Cycasin is a glycoside found in many representatives of the cycads (cycadales) . The aglycon of cycasin is methyl azoxymethanol.
Occurrence
Cycasin occurs in all genera of the cycads, such as Cycas revoluta and Cycas circinalis . Cycasin occurs in all parts of plants, the content is particularly high in young shoots.
Poisonous effect
Cycasin and its aglycon methylazoxymethanol are liver-damaging in humans and rodents and carcinogenic in rodents. Cycasin itself is not yet poisonous, only the aglycon. The substance that ultimately causes cancer is the breakdown product of methyl azoxymethanol, the methyldiazonium ion, which methylates nucleic acids.
In humans, the ingestion of insufficiently purified cycad flour leads to liver damage and neurogenic effects. After 12 to 24 hours, nausea and vomiting occur, and deaths are also known. The high incidence of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) in Guam residents has been linked to regular consumption of cycad flour.
It is also known that livestock, especially cattle and sheep, have been poisoned after consuming cycads. Especially in Australia this poisoning was a big problem for a long time, because in many areas the cycads are the only plants that remain green during the dry season.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c L. Roth, M. Daunderer, K. Kormann: Poison plants, plant poisons . 4th edition, ecomed, Landsberg 1994, p. 798 (reprint ISBN 3-933203-31-7 ).
- ↑ a b c d e Safety Data Sheet Cycasin of the Division of Occupational Health and Safety of the NIH , accessed May 1, 2008.
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ^ A b Loran M. Whitelock: The Cycads . Timber Press, Portland 2002, pp. 48f. ISBN 0-88192-522-5 .

