Triangle generator
A triangle generator is an electronic circuit for generating a triangular wave . Such an oscillation increases linearly up to a maximum voltage value and then decreases linearly up to a minimum voltage value. The triangle generator can be subsumed under the signal generators .
functionality
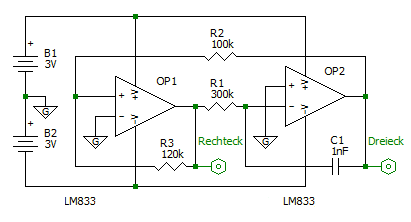
In the case of the analog circuit implementation, the operational amplifier OP2 in the circuit is connected as a Miller integrator and realizes the linear rise and fall. Charging resistor is R1, integration capacitor is C1. OP1 is connected as a non-inverting Schmitt trigger . R2 and R3 determine the switching voltages. If the voltage at the output of the Miller integrator reaches the upper switching voltage of the Schmitt trigger, the voltage at the output of OP1 is switched from almost positive supply voltage to almost negative supply voltage. The Miller integrator integrates these voltage jumps into a triangular signal .
The frequency of the triangular oscillation is determined by R1 and C1.
In addition to the analog circuit technology, a triangle generator can also be implemented in the context of digital signal processing using Direct Digital Synthesis (DDS). In addition to better reproducibility, it has the advantage that the frequency can be set and changed more easily.
Applications
In the case of analog function generators , it is a classic method to convert a triangular wave into a more or less good approximation of a sinusoidal wave using non-linear components .
literature
- Wilhelm Benz, Peter Heinks, Lothar Starke: Electronic and communications engineering table book . 2nd Edition. Frankfurter Fachverlag, Frankfurt 1980, ISBN 3-87234-065-4 .