Echinorhynchus
| Echinorhynchus | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
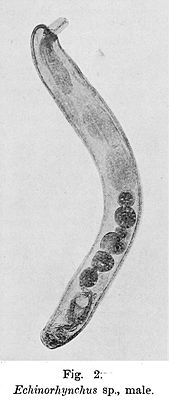
Echinorhynchus sp. |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Echinorhynchus | ||||||||||||
| Zoega in Müller , 1776 emend. Blumenbach , 1779 |
Echinorhynchus is a genus of scratchworms that, as adults, live without exception as intestinal parasites in marine and freshwater fish andtrigger echinorhynchosis in them .
features
The representatives of the genus Echinorhynchus are small to medium-sized species of scratchworms, which like other species of Echinorhynchidae have no spines on their rump. It is characterized by the more or less cylindrical trunk ( Proboscis ) and the corresponding trunk sheath with a ganglion in the central wall region. In addition, the lacunae system of the tegument is connected to one another by numerous anastomoses . The trunk is also equipped with numerous hooks that have simple root processes and become smaller to the trunk base. The males have 6 cement glands.
The eggs of the species are long and spindle-shaped and have typical bulges on the egg poles.
Way of life
The species of the genus Echinorhynchus live as adult animals as an intestinal parasite exclusively in the intestines of fish. There are species that are limited to freshwater fish and others that occur only in marine fish or in both. Small crustaceans such as amphipods or aquatic woodlice act as intermediate hosts .
species
About 80 species are distinguished within the genus. The most popular types include the following:
literature
- Theodor Hiepe, Renate Buchwalder, Siegfried Nickel: Textbook of Parasitology. Volume 3: Veterinary Helminthology. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Jena 1985; Pages 395-397