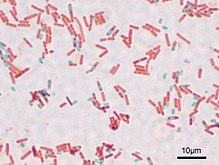
Endospore staining
The endospore staining includes histological methods for coloring endospores of certain bacteria - and fungi . They are used in preparation for a microscopic determination, as the spores usually have shapes and sizes typical of the species.
properties
Methods for endospore staining in bacteria are e.g. B. the Moeller stain with carbol fuchsin and a methylene blue counterstain, the Schaeffer-Fulton stain with malachite green and a safranin counterstain or the Dorner-Snyder stain with carbol fuchsin and nigrosine counterstain used. Since endospores have a relatively tight capsule, the diffusion of the dyes is low, which increases the staining time (min. 30 min). With mushrooms z. B. the PAS staining , the Papanicolau stain , the silver staining according to Grocott and Giemsa staining used.
literature
- J. Reynolds, R. Moyes, DP Breakwell: Differential staining of bacteria: endospore stain. In: Current protocols in microbiology. Appendix 3 J, November 1, 2009, ISSN 1934-8533 , doi: 10.1002 / 9780471729259.mca03js15 , PMID 19885937 .
- Marise Hussey, Anne Zayaitz: Endospore Stain Protocol , American Society for Microbiology , 2011.
Individual evidence
- ^ R S. Mehrotra: Principles of Microbiology . Tata McGraw-Hill Education, 2009, ISBN 978-0-07-014120-9 . P. 54.
- ^ RN Doetsch: Determinative methods of light microscopy. In: P. Gerhardt, RGE Murray, RN Costilow, EW Nester, WA Wood, NR Krieg, GB Phillips (eds.): Manual of methods for general bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, 1981, ISBN 978-0-914826-29-3 . Pp. 21-33.
- ↑ DA Mormak, LE Casida: Study of Bacillus subtilis Endospores in Soil by Use of a Modified Endospore Stain. In: Applied and environmental microbiology. Volume 49, Number 6, June 1985, ISSN 0099-2240 , pp. 1356-1360, PMID 16346801 , PMC 241728 (free full text).
- ↑ Lukas Bubendorf, Georg E. Feichter, Ellen C. Obermann, Günter Klöppel, Wolfgang Remmele, Peter Dalquen, Hans-Heinrich Kreipe: Pathology: Zytopathologie . Springer, 2011, ISBN 978-3-642-04562-2 . P. 69.