Erla 5
| Erla 5 | |
|---|---|
 The Erla Me 5 prototype |
|
| Type: | Sports , school and travel aircraft |
| Design country: | |
| Manufacturer: | |
| First flight: |
July 1932 |
| Production time: |
1932-1938 |
| Number of pieces: |
13 |
The Erla 5 is a German sport and touring aircraft from the 1930s, which, as a light and cheap “people's aircraft”, should help implement the idea of “flying for everyone”. In the end, however, only very few copies were made.
development
Work on the aircraft designed by Franz Xaver Mehr began in his small company in Meckenbeuren, known as Flugzeugbau Friedrichshafen Mehr & von Rüdiger GmbH , in the winter of 1931/1932 and was completed in March. A car engine from 1929, converted by the DKW works in Zschopau , which was tested and approved by the DVL , served as the drive . The first flight of the prototype , initially known as Friedrichshafen Me 5 , was carried out by Alfons Lüber in mid-July 1932 from Konstanz airfield without any complications. The other flights did not cause any problems either, and so the test was ended on August 16 with a four and a half hour long flight at an altitude of 2000 m. In search of a sponsor for the planned production, Franz Xaver Mehr then transported the Me 5 with the wings folded up on a car by road to Zschopau and flew it to the owner of the DKW motorcycle works there, Jørgen Skafte Rasmussen . Rasmussen was positive and decided to start series production at the Erla ironworks . The procurement of materials began in 1932 and at the beginning of May 1933, a second model called the Me 5 a was launched, which had a height reduced by 15 cm and a top speed increased to 120 km / h. This was intended as a model aircraft of a total of eleven small series and was therefore to be flown publicly at the "Large Flight Day of the NSDAP " on June 25, 1933 in Dresden with the hope of subsequent construction contracts. However, since the approval had not been granted by this time, the prototype had to be used. In the meantime it had been registered as Erla Me 5 a around the beginning of 1933 , had received the registration number D-2378 , and was again transported by road to Erla in April 1934, where it was equipped with a DKW engine of 20 hp for presentation flights. The demonstration turned out to be extremely unfavorable due to engine problems and ultimately had to be stopped entirely. The testing and acceptance of the second aircraft was also delayed due to problems with the drive, among other things. It was finally registered as D-2585 in September 1933 . In the meantime, construction of the remaining ten Me 5a had started in July, but only slowly due to the lack of engines, and sales also fell short of expectations. By the end of 1938, however, all eleven production aircraft had been sold. One of these aircraft survived World War II , flew in Germany from 1955 to 1958 and then made it to Switzerland, where it received a new engine and flew for the first time in October 1967.
From 1937 on, Franz Xaver Mehr developed the Erla 5D with enlarged rudder, modified landing gear and Zündapp engine in response to a request from the NSFK for a single-seat training aircraft with a 50-hp engine from the Me 5a. The prototype was completed in June 1938 and exhibited to the public at the Belgrade Air Show in July , but this did not result in any orders. Instead, the only specimen registered as D-YMOP completed a three-continent flight from Europe via Asia to Africa and back with the pilot Friedrich Auermann from April 1 to May 20, 1939, covering around 20,000 km. For this, it had additional tanks in the fuselage and wings, which increased the total volume to 140 l (101 kg) and increased the range to 1500 km. It was subsequently presented at the Aerosalon in Brussels in June 1939 , again without success. Shortly afterwards, from August 2nd to 3rd, 1939, Heinz Gabler set a long-distance world record of 1915 km on the Friedrichshafen – Vännäs route in its class with the Erla 5D . The aircraft had a closed cabin for this flight. It was then added to the German Aviation Collection in Berlin , where its trace is lost in the turmoil of war.
construction
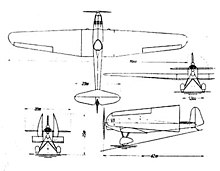
The Erla 5 is a cantilever low-wing aircraft in all-wood construction . The fuselage as well as the supporting structure with a 2.14 ° sweep consist of a wooden structure covered with plywood and partly covered with fabric. The wings are designed to be foldable on the fuselage, which makes it possible to transport the aircraft attached to a car or motorcycle on the road. The rudders of the self-supporting tail unit are covered with fabric, the horizontal and vertical fins are covered with plywood. The series aircraft differ from one another in that they have slightly changed landing gear and, unlike the first prototype, have no main wheels connected to an axle. The Erla 5D has a main undercarriage with a 1.25 m track width and 380 × 150 mm low-pressure tires, other models also use balloon tires.
Technical specifications
| Parameter | Dates (Erla Me 5) | Data (Erla 5 D) |
|---|---|---|
| crew | 1 | |
| span | 11 m | 11.00 m (2.0 m folded) |
| length | 6.20 m | 6.80 m |
| height | 1.75 m | 1.80 m |
| Wing area | 13.7 m² | 14.00 m² |
| Wing extension | 8.06 | |
| V shape | 5.00 ° | |
| Wing loading | 27.5 kg / m² | |
| Power load | 7.70 kg / hp | |
| Area performance | 3.65 hp / m² | |
| Preparation mass | 220 kg | 265 kg |
| Payload | 105 kg (for aerobatics) 120 kg (for sport and cruise flights) |
120 kg |
| Takeoff mass | 325 kg (for aerobatics) 340 kg (for sport and cruise flights) |
385 kg |
| drive | a water-cooled two - cylinder engine with a rigid two-bladed wooden propeller |
an air-cooled, hanging four-cylinder in - line engine with a rigid two-bladed wooden propeller (ø 1.80 m) |
| Type | DKW | Zündapp 9-092 |
| Starting power, climbing power, continuous and travel power |
18 PS (13 kW) at 3500 rpm 16.5 PS (12 kW) at 3500 rpm 14.5 PS (11 kW) at 3000 rpm |
50 hp (37 kW) at 2300 rpm 45 hp (33 kW) at 2225 rpm 40 hp (29 kW) at 2150 rpm |
| Fuel supply | 40 l (29 kg) | |
| Fuel consumption | 13.5-14 l / h for travel services | |
| Top speed | 110 km / h | 160 km / h |
| Cruising speed | 140 km / h | |
| Landing speed | 50 km / h | 62 km / h |
| Rate of climb | 3.50 m / s | |
| Rise time | 6.2 min at 1000 m altitude 15.5 min at 2000 m altitude |
|
| Service ceiling | 4700 m | |
| Range | 430 km or 620 km | |
| Flight duration | 4.5 h | |
literature
- Bruno Lange: Type manual of German aviation technology . In: German aviation . tape 9 . Bernard & Graefe, Koblenz 1986, ISBN 3-7637-5284-6 , pp. 130/131 .
- Werner von Langsdorff : Handbook of aviation . Born in 1939. 2nd, unchanged edition. J. F. Lehmann, Munich 1937, p. 445/446 .
- Heinz J. Nowarra: The German air armament . 2: Erla - Heinkel aircraft types. Bernard & Graefe, Koblenz 1993, ISBN 3-7637-5466-0 , p. 18 .
- Karl-Dieter Seifert: DKW and the Erla Me aircraft 1926–1945 . Sutton, Erfurt 2011, ISBN 978-3-86680-852-2 .
- Helmut Schneider: Airplane type book . Handbook of the German aviation and accessories industry. Reprint of the original edition from 1944. Gondrom, Bindlach 1986, ISBN 3-8112-0484-X , p. 80/81 .