Ethoxy group
| Ethoxy group |
|
|
|
|
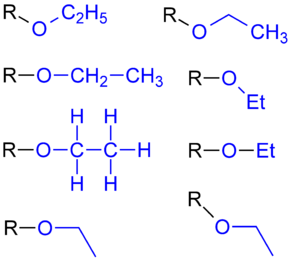
The ethoxy group (ancient ethoxyl group ) is one of the simplest atomic arrangements in organic chemistry, which supplements an ethyl group with a heteroatom (oxygen).
The formula of the substituent is –OC 2 H 5 , sometimes also written as –OEt .
The ethoxy group is not an independent chemical substance, but always part of a larger molecule (see illustration). The smallest molecule in this group is ethanol , which is mostly classified as an alcohol with a hydroxyl group .
properties
Replacing a hydrogen atom in an alkane with an ethoxy group increases polarity and reactivity . For example, ethers are split into alcohols with aqueous acids at higher temperatures. As a first substituent, an ethoxy group has a moderately activating and an ortho (next to) or para (opposite) directing effect in electrophilic aromatic substitution .
Quantitative analytical determination
For the quantitative analytical determination of ethoxy groups, a sample of the substance to be examined is heated to approx. 100 ° C. with excess hydriodic acid and the resulting iodoethane is distilled off. Silver nitrate is added to the latter to an ethanolic solution and the silver iodide formed as a result of hydrolysis of the iodoalkane is determined gravimetrically.
Individual evidence
- ^ Siegfried Hauptmann : Organic Chemistry , 2nd revised edition, VEB Deutscher Verlag für Grundstoffindindustrie, Leipzig, 1985, ISBN 3-342-00280-8 , p. 343.