Farman F.60
| Farman F.60 Goliath | |
|---|---|

|
|
| Type: | Airliner , bomber |
| Design country: | |
| Manufacturer: | |
| First flight: |
January 1919 |
| Number of pieces: |
> 300 |
The Farman F.60 “Goliath” was a twin-engined biplane made by the French manufacturer Avions Henri y Maurice Farman after the First World War . It was used as a passenger plane , transporter and bomber .
history

The Farman F.60 was to be a further development of the Farman F.50 bomber . The cell was largely taken from this series. The first version with the type designation FF.60 - also a bomber - had its rollout in 1918.
However, the emerging interest in civil aviation prompted the brothers Henri and Maurice Farman to redesign the airframe as a passenger version. In January 1919, the Farman F.60 "Goliath", equipped for a crew of two and twelve passengers, took off on its first flight. The cruising speed was 120 km / h and the range was 400 kilometers.
The "Goliath" became a milestone in French civil aviation at the time and in large parts of Europe.
On February 8, 1919, Henri and Maurice Farman founded the Lignes Aériennes Farman, the first French scheduled airline , which later became part of Air France . The first commercial international passenger flight was carried out on that day by factory pilot Lucien Bossoutrot with an F.60 "Goliath". He flew with eleven passengers dressed as military (England did not allow civilian passengers to fly over its territory) that day from Toussus-le-Noble near Paris to Kenley near London. The former Deutsche Luftreederei (DLR) used the F.60 in liner service between Berlin and Weimar .
In April of the same year, Lucien Bossoutrot set a record with four passengers on board. He rose to an altitude of 6,300 meters and stayed there for five minutes. On May 25th there was another ascent with 25 passengers to 5100 meters.
A long-distance record was set in August. The two pilots Bossoutrot and Coupet flew with six passengers on board in 18 hours and 23 minutes a distance of 2050 kilometers from Paris to Casablanca .
CIDNA used the F.60 “Goliath” from France to Romania .
Around 60 machines of the F.60 "Goliath" were built, most of them went to Belgium, Germany, Italy, South America and Czechoslovakia. The F.60 was manufactured under license in Czechoslovakia.
In total, more than 300 F.60 machines were built worldwide. The last F.60 “Goliath” flew in South America until the end of 1933.
Military version
The military version of the F.60 was built in France from 1922. The machines were in use under different type designations.
In 1925 some aircraft designated as F.62 BN4 were delivered to the Soviet Union , with which two squadrons were equipped and which were mostly used for jumping training for the newly emerging airborne troops. In Poland it flew under the designation F.68 with two engines from Gnome & Rhône 9Ab with 420 hp, larger tanks with a range of 1200 km, and 32 Goliaths were used there as the parachutist F.68 BN. They were also represented in Italy and Japan. The Air Force and the Navy of France alone had 60 machines such as the Farman F.60 BN2 "Goliath", a short-range night bomber, or the Farman F-62 BN5 with two 400 hp Lorraine 12Db engines as a fighter-bomber with 7.7 mm automatic cannons and 600 kg bomb load in action.
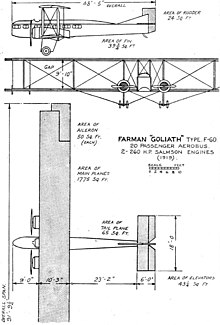
Technical specifications
| Parameter | Data |
|---|---|
| crew | 2 |
| Passengers | 12 |
| length | 14.33 m |
| span | 26.50 m |
| height | 4.91 m |
| Wing area | 161 m² |
| payload | 1330 kg |
| Empty mass | 2500 kg |
| Takeoff mass | 4770 kg |
| Cruising speed | 120–150 km / h at 4000 m above sea level |
| Top speed | 170 km / h |
| Service ceiling | 6300 m |
| Range | 400 km |
| Engines | 2 × Salmson-CM.9 with 9 cylinders, 200 HP (147 kW), 2 four-blade propellers |
See also
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ February 8, 1919 - First international scheduled flight in the world. In: due date. WDR , February 8, 2019, accessed April 13, 2019 .
- ^ Wilfried Copenhagen: Soviet bomb planes. Transpress, Berlin 1989, ISBN 3-344-00391-7 , pp. 105-107