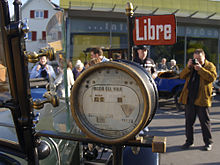taximeter
The meter is an electronic device for detecting fares in taxis based on taxi fares .
overview
The German entrepreneur Friedrich Wilhelm Gustav Bruhn (1853–1927) is considered to be the inventor of the modern taximeter . These fare displays were mounted on horse cabs in the early 1880s and measured the revolutions of the wheel. There are now devices for some vehicle brands that display the fare in the vehicle's interior mirror . Taximeters are often networked with the entire dispatching system of taxi companies. In Germany and Austria, there is a growing desire for automatic receipt creation that replaces filling out forms. For this purpose, specially adapted printers are offered, which enable the printing of taxi receipts and daily statements at the end of a shift .
Fare determination
In Germany it is mandatory that taxis are equipped with a visible and illuminated fare display (i.e. taximeter) ( § 28 BOKraft ). From this, the respective fare can be read, which is usually made up of a basic fee and a kilometer price . In addition, there may be fees for waiting times and other surcharges. In Germany, the tariff is set by the respective district administrative authority, in Austria by the respective governor .
When you switch on the taximeter, the basic fee always appears. The driver can add a surcharge by pressing a button, for example for telephone orders, luggage or night trips. After starting off, the kilometer charge is added by determining the distance traveled and continuously displayed as the fare. During waiting times, for example due to traffic, the device switches from route to time accounting. In order to offer taxi customers precisely calculable prices, some cities in Germany (such as Berlin and Hamburg ) and Austria have now changed the tariff so that the time billing only starts after a certain idle time. As a result, traffic-related waiting times are not calculated, but only requested by the customer, provided that they each exceed a certain period of time. However, new studies have shown that the revenue losses for taxi drivers as a result of this regulation are greater than assumed when it was introduced and that the lack of comparison options with tariffs with classic waiting time calculation leads to distortions of competition . The taximeter is stopped at the destination and the total price is to be paid.
calibration

In Germany, taximeters are checked once a year by the calibration office in order to prove that they are working correctly. If the taximeter is reset by a recognized repairer after a tariff change, the calibration is deemed not to have expired under certain conditions. A subsequent calibration is nevertheless necessary immediately. If everything is in order, the taximeter is provided with a calibration mark and the device is sealed, usually by sticking the calibration mark ( main stamp ) and calibration seal (lead- seal ) on the screws. The calibration is then valid for one year. The taxi company is obliged to take care of the calibration in good time. The calibration mark has a year printed on it. The verification is valid until December 31 of the year which is noted on the verification mark. The new calibration law (MessEG and MessEV) has been in force since January 1, 2015. After this, the year of calibration is shown in the calibration mark. The year of the calibration year is in a diamond on the corner and the calibration mark is always sulfur yellow. After the calibration period has expired or the calibration seal has been removed, the taximeter may no longer be used. A violation of these regulations is an administrative offense.
origin
Devices similar to the taximeter for determining the fare already existed in antiquity. The origin is uncertain, so far there are no sources. A device described by Heron of Alexandria caused a ball to fall into a vessel after a certain distance by hitting a gear construction, the number of balls gave the distance and thus the fare.
For a long time, cabs then drove, followed by taxis with standardized taximeters; there are now a large number of makes that are approved and accepted by the market.
Seat contacts
In order to prevent journeys from being incorrectly recorded, taximeters can sometimes be combined with seat contacts. These contacts register when a passenger takes a seat and automatically start the taximeter. Another variant of these contacts are light barriers in the doors or the center console . Instead of activating the taximeter, these contacts can also be used to log trips not recorded by the taximeter.
Requirements of the tax authorities (Germany)
According to the European Measuring Instruments Directive 2004/22 / EC and its Annex MI-007, it is regulated for the first time that the taximeter must meet the requirements in such a way that the interests of the tax authorities are protected. According to Section 145 (1) sentence 2 AO, it must be possible to track business transactions (here: driving orders) in their creation and processing (individual recording obligation).
The driving order for a taxi is subject to the reduced sales tax rate if the journey takes place within a municipality or if the transport distance does not exceed 50 km ( Section 12 (2) No. 10 UStG ). In order to check whether the reduced tax rate has been applied correctly, the data of the individual driving order must be kept. The letter from the Federal Ministry of Finance dated November 26, 2010 calls for various tax-relevant data to be stored in the taximeter. These requirements apply accordingly to odometers in rental cars (with driver).
The first technical measures are already being implemented to make manipulation of sales figures impossible. In Hamburg, taxis are already being converted to use the INSIKA system. Appropriate preparations are underway in Berlin. The term fiscal taximeter is sometimes used for appropriately modified taximeters .
Situation in other countries
In other countries such as France or Spain, fares often depend on the condition of the vehicle and the policies of the local companies and their national regulations. In some European countries, the use of receipt printers is even mandatory. This trend is increasing internationally. In the meantime, the introduction of fiscal taximeters is also increasingly discussed.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Patent AT47392B : Combined display for fare and surcharges for fare displays . Published on April 10, 1911 , inventor: Friedrich Wilhelm Gustav Bruhn.
- ↑ Sven Althorn: MINUTE OF LEAVE: New test drives document considerable losses. In: TAXI-MAGAZIN.de. Retrieved May 9, 2015 .
- ↑ Sven Althorn: TAXI TARIFF: The hamburger fare compared to other cities. In: TAXI-MAGAZIN.de. Retrieved May 9, 2015 .
- ↑ Eichdirektion-Nord on the subject of the validity of taximeter badges
- ^ Gerhard Löwe, Heinrich Alexander Stoll: Taximeter . In: The ancient world in brief . Koehler & Amelang, Leipzig 1969.
- ↑ Ser. No. 20 of Appendix MI-007
- ↑ BStBl 2010, Part I, p. 342.
- ↑ Funding for taximeters in Hamburg. (No longer available online.) City of Hamburg, traffic trade supervisory authority, archived from the original on February 22, 2013 ; accessed on January 31, 2013 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ^ Report of the BZ Berlin on the introduction of the fiscal taximeter from April 10, 2013.