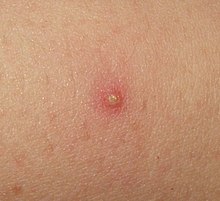
Folliculitis
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| L73.9 | Disease of hair follicles, unspecified |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
In the Folliculitis is an inflammation of the upper (outer) portion of a hair follicle , the infundibulum . Mostly this is caused by the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus .
Folliculitis can occur on all hairy parts of the body. Preferred sites ( predilection sites ) are hairy scalp, chest and trunk area. Hairy men are particularly affected in hot summer months, when increased sweating also promotes bacterial growth. Folliculitis can be very painful, but the resulting papules or pustules usually heal without consequences; the hair follicle remains. When the follicle outlet is clogged by swelling horn material and especially in cases of reduced immune system, the inflammation can spread to the entire hair follicle and thus lead to the development of a boil ; an abscess is created by spreading further into the surrounding tissue. Both must be operationally refurbished.
Special forms
The eosinophilic pustular folliculitis - syn .: Ofuji syndrome, sterile eosinophilic pustulosis - is described for the first time in 1965, almost endemic in Japan (for young men) skin disease with involvement of the face, trunk and extremities. Eosinophilic infiltrates can be detected histologically . The special similarity to dermatoses in the context of an AIDS disease is remarkable . The cause of the disease is unknown. In dogs, eosinophilic facial folliculitis is similar to this condition.
Folliculitis barbae candidomycetica is a very rare Candida infection that can also lead to perifolliculitis. As an infection of deeper skin layers, it must be treated systemically with fluconazole or itraconazole for several weeks to ensure complete healing ( restitutio ad integrum ).
Folliculitis decalvans is a rare, chronic folliculitis of the scalp that leads to the destruction of the hair follicles. The result is scarred alopecia .
The gram negative folliculitis is a chronic relapsing form, caused by the displacement of the normal bacterial flora of the skin with Gram-negative pathogens such as Enterobacter , Klebsiella , Proteus , Escherichia coli or Pseudomonas . The trigger can be long-term antibiotic therapy with mainly gram-positive effects (e.g. erythromycin topical for acne vulgaris ).
literature
- DL Stulberg, MA Penrod, RA Blatny: Common bacterial skin infections . In: Am Fam Physician , 2002 Jul 1, 66 (1), pp. 119-124. Review. PMID 12126026
Individual evidence
- ↑ S. Ise, S. Ofuji: Subcorneal pustular dermatosis. A follicular variant? In: Archives of Dermatology . tape 92 , no. 2 , August 1, 1965, p. 169-171 , PMID 11850921 .