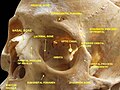
Supraorbital foramen
The foramen supraorbitale ( Latin foramen , "opening"; supra "over"; orbis "circle") is a small bone canal in the frontal bone (os frontale), just above the orbital margin . It lies above the eyebrows , at the transition between the medial and middle third of the frontal bone, 2.3–2.9 cm lateral to the midline of the facial skull . The supraorbital nerve (eyeball nerve ), the first branch of the fifth cranial nerve (V 1 ), the trigeminal nerve , ramus lateralis, and the arteria and vena supraorbitalis pass through it . It occurs in pairs, above the respective orbital margin.
Supraorbital notch
Instead of a foramen, the anatomical deviation is merely a retraction, which is then called the supraorbital incisura .
Trigeminal pressure point
The supraorbital foramen is one of the trigeminal pressure points ( Valleix pressure points ) which react painfully to pressure when the stimulus threshold is reduced, which occurs symptomatically in trigeminal neuralgia . Trigeminal neuralgia is characterized by spontaneous or triggered, lightning-like shooting pain in the area of one or more trigeminal branches, the first branch being rarely affected.
Conduction anesthesia
During surgical interventions on the soft facial tissues in the area of the forehead, conduction anesthesia is applied to the supraorbital foramen.
Individual evidence
- ^ Gerhard Aumüller, Jürgen Engele, Joachim Kirsch, Siegfried Mense: Dual series anatomy . Thieme, 2014, ISBN 978-3-13-152863-6 , pp. 942 ( google.com ).
- ^ Gerhard Aumüller, Jürgen Engele, Joachim Kirsch, Siegfried Mense: Dual series anatomy . Thieme, 2014, ISBN 978-3-13-152863-6 , pp. 990 ( google.com ).
- ↑ Norbert Schwenzer, Michael Ehrenfeld: Surgical basics . Georg Thieme, 2008, ISBN 978-3-13-159084-8 , p. 284 ( google.com ).