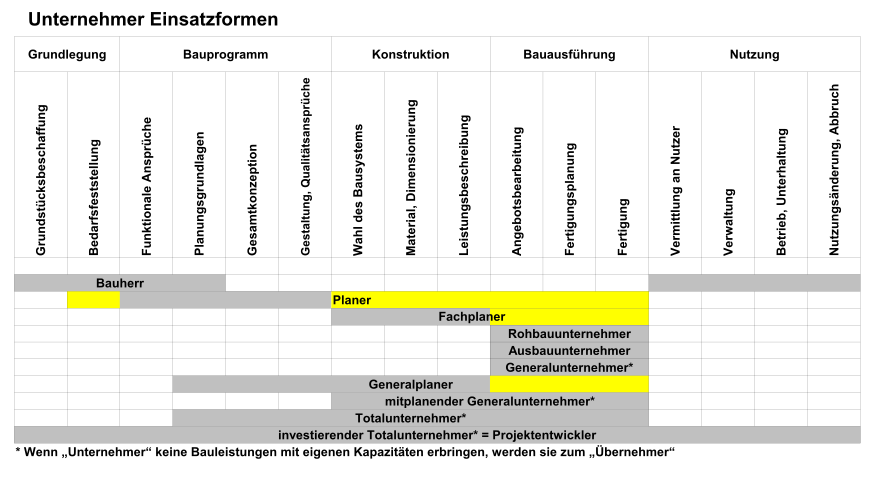
General contractor
As a rule, the general contractor (GU) provides all construction services for the construction of a building. The building is therefore usually built turnkey by the general contractor ( turnkey construction ). This form of construction contract as a type of work contract is known as a general contractor contract.
overview
In contrast to the sole contractor, the general contractor has agreed with the client that he may subcontract (partial) services to subcontractors . However, this does not change the fact that the general contractor is the only contractual partner of the client and has full responsibility for the overall performance.
The general contractor in the narrower sense must provide at least part of the construction work in its own company. He can pass on the remaining services to subcontractors. However, planning services are not included in the scope of the general contractor services . Colloquially , the following forms of entrepreneurship are often referred to as a general contractor : If an entrepreneur awards all services and thus does not create anything in his own company, one speaks of a general contractor . If the planning services are also taken over, one speaks of a total contractor (with personal contribution) or total contractor (without personal contribution).
Construction works are often advertised functionally in general contractor contracts. In addition, the remuneration for the general contractor is regularly flat-rate.
Part-general contractor
In the general contractor contract, the general contractor is usually commissioned with the entire turnkey construction of a building. If only several trades are awarded to a general contractor, one also speaks of a partial general contractor. One example is the award of building construction as well as roof and facade to an entrepreneur. The entire building technology or various facade trades are often bundled in partial general contractor contracts.
advantages
For the client, the general contractor assignment offers the advantage that he or the planner commissioned by him does not have to take over the coordination of the individual trades . Even in the case of defects that cannot be clearly assigned when the entrepreneur is involved in a trade, he only needs to contact the general contractor.
disadvantage
A higher price level is often stated as a disadvantage of awarding general contractors. The general contractor undoubtedly needs additional remuneration for his coordination services. As a rule, the general contractor will therefore add a so-called general contractor surcharge to the prices of the subcontractors commissioned by him. It is often stated that the general contractor contract would be between 10% and 15% more expensive than the remuneration resulting from the sum of all contracts to individual entrepreneurs. However, this can be countered by the fact that the builder saves himself considerable coordination tasks and transfers risks (deadline risks, coordination risks, interface risks) to the general contractor. These are to be assessed in terms of costs. It should also be noted that the general contractor often has greater market experience than the client (building owner) and can therefore generally bind subcontractors who can provide the service more cost-effectively. This purchase benefit is usually passed on to the client. Whether a general contractor is more expensive or cheaper can only be estimated on a project-specific basis.
Entrepreneur application forms
Similar work or delivery contract structures also play a role in other branches of the economy . In general, outside of the construction industry , one speaks of a main contractor who subcontracts part of his work to be provided to the client or purchaser (e.g. in the transport industry ), or of a main supplier who supplies the components, goods and services he is responsible for Requires the fulfillment of an order, partly obtained from sub- suppliers who may not have a direct business relationship with the customer (e.g. in the automotive industry ).
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ Definition in the Gabler Business Dictionary, last accessed on April 16, 2019.
- ↑ Definition in the German bulletin, last accessed on April 16, 2019.
- ↑ "How does the general contractor principle work?" in the guide "Construction companies - find and order construction companies" on gelbeseiten.de; last accessed on April 16, 2019.