Die
Dies are tools for forming processing that contain the cavity (negative form) of at least part of the workpiece.
Drop forging
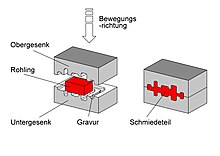
In closed-die forging, a die is understood to be a forming tool in the form of an at least two-part hollow form made of heat-resistant tool steel . Dies are at forging under mechanical forging hammers, such as pneumatic hammers or forging presses ( hydraulic press ) is used traditionally by the blacksmith z. B. by a sledgehammer .
The required geometry of the forging is made in the form of a split engraving in the two halves of the die. The exact shape of this engraving results from the shape of the part to be forged, the material flow, the resulting burr on the forging and other technological requirements.
The state of the art is the previous simulation of the forging process with the help of simulation software in order to identify and prevent possible flow errors (e.g. overfolding in the material) or underfilling directly when designing the engraving of the die.
The production of the die is done on modern CNC -controlled machine tools ( HSC - milling or spark erosion machines ).
To bend
When bending a sheet metal part on a press brake , the workpiece is pressed into the V-shaped die. A detailed description of the process variants can be found in the article bending .