Glutaminase
| Glutaminase | ||
|---|---|---|
|
||
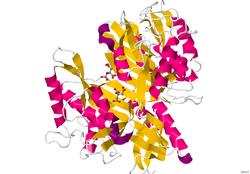
| Crystallographic structure of a glutaminase protein dimer from Chryseobacterium proteolyticum . | ||
| Secondary to quaternary structure | Homodimer | |
| Isoforms | 3 | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene name (s) | GLS GLS2 | |
| External IDs |
|
|
| Enzyme classification | ||
| EC, category | 3.5.1.2 , hydrolase | |
| Response type | Deamination | |
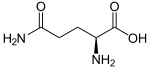
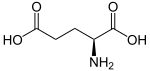
| Substrate | L-glutamine + H 2 O | |
| Products | L-glutamate + NH 3 | |
| Occurrence | ||
| Parent taxon | Creature | |
The glutaminases ( L -Glutaminamidohydrolasen) are enzymes from the group of amidases (also amidohydrolases ) consisting of the amino acid glutamine with absorption of water (H 2 O) and release of ammonia (NH 3 ) glutamate produce. Glutaminases are found in the nerve and glial cells of all higher living beings and can be activated by phosphates and calcium ions (Ca 2+ ).
Catalyzed equilibrium
The hydrolysis of L -glutamine produces L -glutamate and ammonia. This reaction is the first step in glutaminolysis .
Individual evidence
- ↑ PDB 3A56 ; Hashizume R, Mizutani K, Takahashi N, Matsubara H, Matsunaga A, Yamaguchi S, Mikami B: Crystal structure of protein-glutaminase . In: to be published . 2010. doi : 10.2210 / pdb3a56 / pdb .
- ^ Wissenschaft-Online-Lexika: Entry on glutaminase in the Lexikon der Neuroswissenschaft , accessed on December 5, 2012.