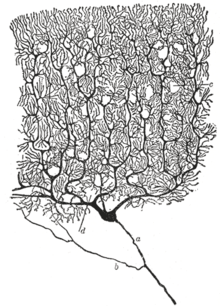
Golgi stain
The Golgi staining (synonymous Golgi method ) is a biochemical method for silver staining of tissue sections .
principle
The Golgi staining, like the silver staining of polyacrylamide gels , is based on the binding of silver ions to argyrophilic biomolecules . However, the silver ions are not converted into black-brown elemental silver by subsequent reduction , but are precipitated as an insoluble salt ( silver chromate ) at the binding site . Through the addition of silver chromate to crystal nucleiA locally increased concentration of silver chromate occurs in the nerve cells. Only a few neurons are stained, but these are completely colored. This allows viewing of individual neurons in neuronal tissue, while other methods of staining stain the entire tissue.
For Golgi staining, the fixed tissue sections are treated with a two percent potassium dichromate solution for two days and then with a two percent silver nitrate solution for two days , after which silver chromate precipitates in the tissue on the crystallization nuclei. The Golgi stain was further developed by Ramón y Cajal, Colonnier (1964) and Strausfeld (1980). The Golgi staining can be combined with the Nissl staining .
history
The Golgi stain was developed in 1873 by the later Nobel Prize winner Camillo Golgi for contrasting nerve tissues ; it was later referred to as “la reazione nera” ('the black reaction'). Nobel laureate Santiago Ramón y Cajal used and modified Golgi stain to further determine neural anatomy . For their knowledge of the structure of nerves, both were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1906.
Golgi staining is based on the development of photographs and was their first application in tissues . This developed in the 19th century from Thomas Wedgwood's photograms , followed by the daguerreotype and the calotype . Golgi staining has been used extensively for over 30 years. The method was replaced by other colors between the world wars. It has been used more frequently since the advent of the transmission electron microscope .
literature
- RS Williams: Golgi's method of staining nerve cells. In: Journal of neuropathology and experimental neurology. tape 42 , no. 2 , March 1983, ISSN 0022-3069 , pp. 210-212 , PMID 6186778 (English).
- Gold and Silver Staining: Techniques in Molecular Morphology . In: Gerhard W. Hacker, Jiang Gu (Eds.): Advances in Pathology, Microscopy, & Molecular Morphology . CRC Press, Boca Raton 2002, ISBN 1-4200-4023-5 (English, 264 pages, limited preview in Google Book Search).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c E. Pannese: The Golgi Stain: invention, diffusion and impact on neurosciences. In: Journal of the history of the neurosciences. Volume 8, Number 2, August 1999, ISSN 0964-704X , pp. 132-140, doi: 10.1076 / jhin.8.2.132.1847 . PMID 11624294 .
- ↑ JG Nicholls: From neuron to brain. Sinauer Associates, 2001. ISBN 0-87893-439-1 . P. 5.
- ↑ M. Colonnier: The tangential organization of the visual cortex. In: Journal of Anatomy . Volume 98, July 1964, ISSN 0021-8782 , pp. 327-344. PMID 14193193 . PMC 1261360 (free full text).
- ^ Nicholas James Strausfeld: The Golgi method: Its application to the insect nervous system and the phenomenon of stochastic impregnation. In: NJ Strausfeld, TA Miller (Ed.): Neuroanatomical Techniques. Insect Nervous System. Springer, New York 1980, ISBN 1-4612-6020-5 , pp. 132-205.
- ↑ N. Pilati, M. Barker, S. Panteleimonitis, R. Donga, M. Hamann: A rapid method combining Golgi and Nissl staining to study neuronal morphology and cytoarchitecture. In: The journal of histochemistry and cytochemistry: official journal of the Histochemistry Society. Volume 56, Number 6, June 2008, ISSN 0022-1554 , pp. 539-550, doi: 10.1369 / jhc.2008.950246 . PMID 18285350 . PMC 2386766 (free full text).
- ^ G. Grant: How the 1906 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was shared between Golgi and Cajal . In: Brain Res Rev . tape 55 , no. 2 , October 2007, p. 490-498 , doi : 10.1016 / j.brainresrev.2006.11.004 , PMID 17306375 .
- ^ C. Golgi: Sulla struttura della sostanza grigia del cervello. In: Gazzetta Medica Italiana (Lombardia) . tape 33 , 1873, pp. 244-246 .
- ^ A. Dewulf: The significance of the works of Ramón y Cajal carried out with Golgi's method. In: Acta neurologica et psychiatrica Belgica. Volume 54, Number 7, July 1954, ISSN 0001-6284 , pp. 545-555. PMID 13206711 .
- ↑ T. Wedgwood, H. Davy: An account of a method of copying paintings upon glass and making profiles by the agency of light upon nitrate of silver, invented by T. Wedgwood, Esq., With observations by H. Davy. In: Journal of the Royal Institution. Volume 1, No. 9, London, June 22, 1802.