Harmonic Drive
A Harmonic Drive (also voltage wave transmission , the wave gear , sliding wedge , or by the English designation strain wave gear (SWG)) is a gear with an elastic transmission member by high translation and stiffness distinguished. The first stress wave transmission was developed by Walton Musser in 1955. Harmonic Drive SE manufactured the first wave gears in series production under the product name or the registered trademark Harmonic Drive .
construction
A stress wave transmission consists of three elements:
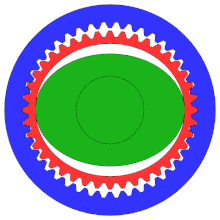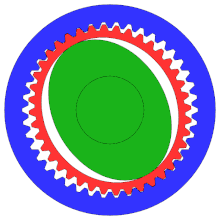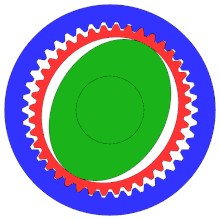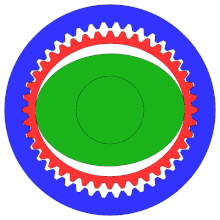
- an elliptical steel disc with a shrunk-on roller bearing and a thin, deformable race, the so-called wave generator . The harmonic drive shown works without a rolling bearing ring. The elliptical steel disk drives the gearbox. It is drawn in green on the right.
- a deformable cylindrical steel liner with external teeth , the so-called Flexspline . The steel sleeve is the output. On the right it is red.
- a rigid cylindrical outer ring with internal teeth , the circular spline . At the bottom and top, its teeth and those of the Flexspline interlock. It's blue on the right.
The external teeth of the steel sleeve have fewer teeth than the internal teeth of the outer ring. Usually this difference is two teeth. Flexspline and Circular Spline thus perform a relative movement of two teeth with each revolution.
functionality
The driven elliptical disc deforms the thin-walled steel sleeve over the outer ring of the ball bearing. As a result, the external toothing of the steel sleeve engages with the internal toothing of the outer ring in the area of the large axis of the ellipse. If you hold on to the outer ring, the steel bushing (the output) remains behind with one revolution of the drive pulley, corresponding to the smaller number of teeth compared to the outer ring.
The high number of teeth of the fine toothing results in very large reductions. For example, with z = 200 teeth for the internal toothing and z = 198 for the steel sleeve 198: 2 = 99, if the elliptical disk is defined as the drive and the steel sleeve as the output. For 99 revolutions of the elliptical disc, the deformable steel sleeve rotates once.
Approx. 30% of the teeth take part in the power transmission. Together with the high reduction ratio of 30: 1 up to 320: 1, the harmonic drive is torsionally rigid and free of backlash. Depending on the version, the positioning accuracy is better than 30 arc seconds. The gearbox is compact and maintenance-free . Wave gears are used for axle drives in robots, drives in flight simulators , the tracking of large parabolic antennas , in motor vehicles ( dynamic steering ), in machine tools and in drives for printing machines.
Another backlash-free gear for transmitting large torques is the cycloid gear . The cycloid gear is more efficient than the strain wave gear (95 percent compared to 85 percent), but is more complex to manufacture.
application
The moon car of the Apollo space program was driven by a 180 W electric motor per wheel, which was connected to it via a harmonic drive gear with 80: 1 reduction.
literature
- Dipl.-Ing. Ullrich Höltkemeier: It's the principle that counts , in: Konstruktionspraxis Spezial Antriebstechnik, March 2013, page 80 ( PDF ) ( page no longer available )
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Georg Jacobs (Ed.): Maschinengestaltung Volume II. Verlag Mainz, Aachen 2016, ISBN 978-3-86130-749-5 , p. 249 f.
- ↑ Patent US2906143A : Strain wave gearing. Applied March 21, 1955 , published September 29, 1959 , applicant: United Shoe Machinery Corp., inventor: Walton Musser.