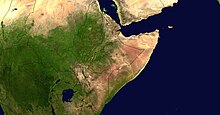
Horn of Africa
Horn of Africa describes the easternmost part of the African continent , which juts out into the Indian Ocean in a wedge shape and includes the Gulf of Aden on its north side . The Horn includes the states of Somalia , Ethiopia , Djibouti and Eritrea . Since the Somali civil war that began in 1988, the autonomous region of Puntland , located directly at the tip of the Horn, and the de facto regime Somaliland have split off from Somalia . The coastal region of this headland is called the Somali Peninsula .
The term Horn of Africa has been in use in the media especially since the Ogaden War between Somalia and Ethiopia in 1977/78 over the Ogaden region . In 2011 there was a severe hunger crisis in the Horn of Africa due to drought , which according to reports from international organizations affected 11.5 million people (as of August 2011).
ecology
The Horn of Africa is one of only two biodiversity hotspots in the arid area of the earth. The region suffers above all from excessive grazing pressure ("overgrazing"), which has led to a great loss of habitat. Only five percent of the original ecosystem has been preserved. In the Socotra Archipelago, fishing and the increasing sealing of the landscape are a major problem.
Regional security aspects
To stabilize the region, the EU's multinational Operation Atalanta was launched to protect humanitarian aid shipments to Somalia, to protect the free sea and to combat piracy off the Somali coast.
literature
- History guide: Horn of Africa. On behalf of the Military History Research Office, ed. by Dieter H. Kollmer and Andreas Mückusch. Schöningh, Paderborn et al. 2007, ISBN 978-3-506-76397-6 , p. 288.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Horn of Africa Drought Crisis Situation Report No. 5 (PDF; 171 kB). OCHA, July 21, 2011.