Invert sugar
Invert sugar ( invertose , sometimes also trimoline ) is a mixture of grape sugar ( glucose ) and fruit sugar ( fructose ), which is produced by breaking down table sugar ( sucrose ) or starch . The term invert sugar refers to the changed effect of the sugar solution on the vibration level of light, because after the breakdown of sucrose to invert sugar, the sugar solution changes its optical activity from clockwise to counterclockwise . This change in optical activity is called inversion .
The conversion of nectar into honey is based in part on the same principle. In contrast to invert sugar , isoglucose , which also consists of glucose and fructose, is not produced by breaking down sucrose, but rather by partially converting glucose into fructose.
Manufacturing
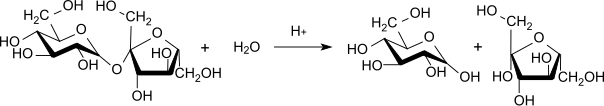
Invert sugar is produced by adding small amounts of acid as a catalyst to sucrose ( cane or beet sugar ) dissolved in hot water or by treating it with invertase . The sucrose molecules , which are composed as disaccharides from one grape and one fructose molecule , are broken down again into their two monosaccharide components:
This chemical process is known as hydrolysis (the specific case of cane sugar inversion ). With the help of polarized light you can keep track of how far the reaction has progressed with a polarimeter . At the beginning the sample consists almost entirely of sucrose , which has a specific angle of rotation of + 66.5 °. As the reaction progresses, the sucrose breaks down into glucose with a specific angle of rotation of + 52 ° and fructose -92 °. Since the directions of rotation of the two substances overlap, the finished invert sugar has a specific angle of rotation of −20 °, i.e. the arithmetic mean between the two individual values that are far apart.
Invert sugar can also be produced by microorganisms (certain strains of yeast) or with immobilized invertase.
use
Invert sugar is processed into liquid sugar or invert sugar cream (previously called artificial honey ) or used as invert sugar syrup in the food industry, similar to glucose syrup . Invert sugar syrup is also used for winter feeding in beekeeping and as an additive in the tobacco of many cigarette brands . In the list of ingredients on food packaging, glucose-fructose syrup is increasingly being used instead of invert sugar syrup , as this is now more often made from starch instead of sucrose. Commercial sugar syrup for cocktails also consists mainly of water and invert sugar. Invert sugar tastes a bit milder and more fruit-like than non-inverted sucrose. In addition, it does not crystallize as easily as sucrose, so that the cream or syrup remains liquid longer than an equally concentrated sucrose solution. Fructose is mainly responsible for this, as it is highly hygroscopic and difficult to crystallize. The most common invert sugar syrup has a concentration of 72.7% and an inversion degree of 66%. One liter of this syrup has the same sugar content and the same sweetness as one kilogram of normal household sugar, which is to be expected due to the density of approx. 1.375 kg / l.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet: Biochemistry, 4th Edition. John Wiley & Sons, 2010, ISBN 978-1-118-13993-6 . P. 367.
- ↑ Ternes, Täufel, Tunger, Zobel: food dictionary , Behr's Verlag, 4th Edition 2005, ISBN 3-89947-165-2 .
- ↑ Additives in cigarettes at Rauchfrei.de.
- ↑ K. Rosenplenter, Ulrich Nöhle, Gert-Wolfhard von Rymon Lipinski: Handbook sweeteners: Properties and application , Behr's Verlag, 2007, ISBN 978-3-89947262-2 .