Isoindole
| Structural formula | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
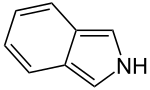
|
||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Surname | Isoindole | |||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 7 N | |||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | 117.15 g mol −1 | |||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||
Isoindole is a chemical compound from the group of bicyclic heteroaromatics and is the nitrogen analogue of isobenzofuran . It is made up of a pyrrole ring and a fused benzene ring. It is isomeric to indole . The compound forms the basic structure of other chemical compounds such as phthalocyanines .
Appearance and properties
Isoindole can be prepared by vacuum - pyrolysis or a retro Diels-Alder reaction are obtained.
It is unstable and converts at temperatures above −40 ° C. Depending on the conditions, the compound is in two tautomeric forms (2 H -isoindole and 1 H -isoindole / 1 H -isoindolenine) or an equilibrium of the two forms, the predominant form generally depending on the substituent in the case of substituted isoindoles.
Individual evidence
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ^ Karl M Kadish, Kevin Smith, Roger Guilard: Handbook of Porphyrin Science: Synthesis and structural studies . World Scientific, 2010, ISBN 981-4322-35-0 , pp. 38 ( limited preview in Google Book search).

