Joint Direct Attack Ammunition
Joint Direct Attack Munition , shortly JDAM (German about Direct Attack Munitions for associated forces ), is a retrofit kit for various unguided bombs of the United States Armed Forces and other nations. The now precision-guided bombs upgraded in this wayare also referred to as JDAM. The steering is usually carried out by a combined INS / GPS system, with conversion kits with laser aiming systems also being available. JDAMs have been around since the Kosovo Warused in very large numbers in 1999 (well over 10,000 times) and are one of the most important air-to-ground weapon systems in the western world. The price of a retrofit kit for by far the most widely used bomb bodies of the Mk-80 series is currently (as of 2011) around 30,000 US dollars .
variants

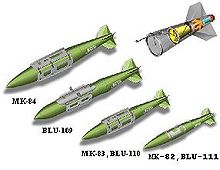
| designation | Weight class | Available warheads |
length | diameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GBU-31 | ~ 1000 kg | Mk 84 , BLU-109 , BLU-117 | 3.88 m | 46 cm |
| BLU-119 | 3.77 m | 37 cm | ||
| GBU-32 | ~ 500 kg | Mk 83 , BLU-110 | 3.04 m | 36 cm |
| GBU-38 | ~ 250 kg | Mk 82 , BLU-111 |
Other versions and names
- GBU-29: 2000 pounds / 907 kg , not produced by Martin Marietta
- GBU-30: 1000 pounds / 454 kg, Martin-Marietta, not produced
- GBU-34: BLU-116 (2000 pounds / 907 kg) warhead , Lockheed Martin , not produced
- GBU-35: Warhead BLU-110 (1000 pounds / 454 kg), old designation of the US Navy GBU-32
- GBU-52: GBU-31 (2000 pounds / 907 kg) with laser sensor (LJDAM)
- GBU-54: GBU-38 (500 pounds / 227 kg) with laser sensor (LJDAM)
Laser-guided variants (LJDAM)
With the Laser Joint Direct Attack Ammunition (LJDAM, GBU-5 x ), Boeing developed a variant with a laser sensor. It can also be used against moving targets, but only when visibility is good. If necessary, the sensor module would be mounted on the tip of the bomb shortly before use. On June 30, 2006, a US Air Force F-16 successfully tested a 500 pound (227 kilograms ) LJDAM against a moving armored transporter. On May 18, 2007, Boeing won an initial contract to supply 600 laser sensor modules for $ 28.8 million.
development
In 1992, the USA began developing precision-guided bombs, which were intended to increase the accuracy of bombings from medium and high altitudes, even in poor visibility. With a retrofit kit designed by McDonnell Douglas ( Boeing since 1997 ) from 1995 onwards , conventional unguided (“stupid”) free-fall bombs can be converted into guided (“smart”) bombs. Originally, the purchase of 87,000 units was planned, which should be used by all combat aircraft and bombers of the US Air Force and the US Navy . During the testing period from 1998 to 1999, more than 450 JDAMs were used. JDAM first came into combat on March 24, 1999 in the Kosovo war , when two B-2 bombers each dropped 16 such bombs on Serbian targets.
technology
The JDAM extension consists of a navigation module equipped with control surfaces that is mounted on the tail of an unguided bomb. After releasing, the bomb is steered into the programmed target using inertial navigation and GPS support. Thrown from a great height, the range is around 28 kilometers. For accuracy, the Air Force gives a circle error probability of 13 meters when GPS is used. 2005 A retrofit kit cost an average of around 22,000 US dollars .
Platforms
They can be used by the following platforms:
- A-10C Thunderbolt II
- B-1B
- B-2A Spirit
- B-52H Stratofortress
- F-15E Strike Eagle
- F-22 Raptor
- F-16C / D Fighting Falcon
- AV-8B Plus Harrier II
- F / A-18C / D Hornet and F / A-18E / F Superhornet of the U.S. Navy and Marine Corps
- MQ-9 ,
- Mirage 2000D
- Filipino OV-10D Bronco
- A-4 Skyhawk
- AMX
- German Panavia Tornado
- Mitsubishi F-2A / B
- KAI TA / FA-50 Golden Eagle
It is planned to use it with the F-35 Lightning II .
commitment
From 1999 to early 2006, over 15,000 JDAMs were dropped. The planned production target is 217,746 JDAM bombs by 2011, of which 149,237 for the Air Force and 68,509 for the US Navy. Boeing also has 18 other international customers for this type of bomb; Israel started in 2000 , followed by Australia , Germany , Great Britain and Norway , among others .
On July 24, 2008, the German Air Force ordered LJDAM kits which, in addition to GPS navigation, can also be guided to the target by laser. Testing by the WTD 61 on the tornado was successfully completed at the end of 2009.
literature
- Andreas Parsch: Boeing JDAM. In: Directory of US Military Rockets and Missiles. August 21, 2008, accessed January 11, 2013 .
Web links
- Information of the US Air Force for JDAM (English)
- Joint Direct Attack Munition (JDAM) at FAS (English)
Individual evidence
- ↑ DEPARTMENT OF THE NAVY FISCAL YEAR (FY) 2006 / FY 2007 BUDGET ESTIMATES
- ↑ a b GAF Tornado Integrates Laser JDAM Weapon. In: Airforce Technology. December 7, 2009, accessed January 11, 2013 .