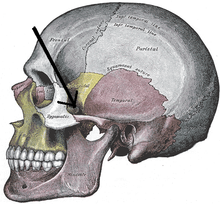
Zygomatic arch

The zygomatic arch ( Latin Arcus zygomaticus ) is a strong bony ridge of the skull in mammals . It starts below the eye socket and moves horizontally towards the ear . The zygomatic arch can easily be felt through the skin.
The zygomatic arch is composed of two bone processes. The temporal bone process of the zygomatic bone ( processus temporalis ossis zygomatici ) forms the front section, the zygomatic process of the temporal bone ( processus zygomaticus ossis temporalis ) the rear. Both processes are connected to one another by an oblique bone suture . Above the external auditory canal, the zygomatic arch continues in a shallow bone ridge ( crista supramastoidea ) on the temporal bone scale . The frontal process of the zygomatic bone ( processus frontalis ossis zygomatici ) extends upwards from the temporal bone process , which limits the eye socket at the back. In predators , this process is very short and does not unite with the zygomatic process of the frontal bone ( processus zygomaticus ossis frontalis ).
The zygomatic arch delimited laterally and below the temporal fossa ( temporal fossa ). Its upper edge serves the attachment of the fascia of the temporal region ( Fascia temporalis ), the lower edge serves the origin of the muscle masseter , the most important masseter muscle .
literature
- Franz-Viktor Salomon: Bony skeleton . In: Franz-Viktor Salomon et al. (Hrsg.): Anatomie für die Tiermedizin. 2nd ext. Ed., Enke-Verlag, Stuttgart 2008, ISBN 978-3-8304-1075-1 , pp. 37-110.
- Eduhard Hallmann : The comparative osteology of the temporal bone - to simplify the prevailing views, Hahn'sche Hofbuchhandlung, Hanover, 1837