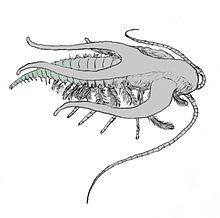
Kaili fauna
The Kaili fauna ( 凯里 生物 群 , Kǎilǐ shēngwù qún ), also Kaili biota or Kaili faunal community , is a Central Cambrian conservation deposit of the Burgess slate type. It comes from the middle section of the Kaili Formation in Guizhou Province in the People's Republic of China and is about 510 to 505 million years old.
Fossil content
The fossil content of the Kaili Formation is extremely diverse and contains 110 different genera (including algae even more than 130 genera) belonging to 11 tribes . Forty of these 110 genera are equally represented in the somewhat younger Burgess slate and thirty genera can be found in the older Maotianshan slate . Hard shellfish such as trilobites and echinoderms ( Eocrinoidea ) are predominant , but there are also genera with soft body preservation. Parvancorina , an arthropod that already occurs in the Neoproterozoic, serves as an example . Notable for the Kaili fauna are finds that are interpreted as eggs and embryos of invertebrates. Of importance also are acritarchs that naraoiidae that Chancelloriidae and arthropods such. B. Marrella .
List of Kaili fauna sorted by tribes (selection)
Reich Protista (seaweed)
This includes brown algae , green algae and coralline red algae .
- Enteromphites siniansis
- Fractibeltia fibrilata
- Marpolia spissa - possibly a cyanobacterium ?
- Thamonphyton formosus
Acritarches
- Cristallinium cambriense
- Cristallinium dabium
- Dictyotidium sp.
- Granomarginata great
- Granomarginata squamacea
- Leiofusa sp.
- Micrhystridium brevicorum
- Micrhystridium pallidum
- Pterospermella solida
- Retisphaeridium howelli
Phylum Annelida (annelids)
- Pollingeria sp.
Phylum Arthropoda (arthropod)
- Anomalocaris sp.
- Canadaspis sp.
- Isoxys cf. auritus
- Marrella
- Mollisonia sinica
- Naraoia sp.
- Tuzoia bispinosa
Phylum Arthropoda - class Trilobita
- Pagetina sp. - order Agnostida
- Curvoryctocephalus taijiangensis - order Corynexochida
- Olenoides paraptus
- Oryctocephalina indicus
- Oryctocephalina yui
- Eosoptychoparia spinosa - order Ptychopariida
- Xingrenaspis xingrenus
- Kaotai globesa ?
Tribe Brachiopoda (armpods)
- Glyptacrothele bohemica - order Lingulida
- Nisusia katujensis - order Orthida
Phylum Echinodermata ( Echinoderms )
- Balangicystis sp. - Class Eocrinoidea
- Sinoeocrinus globe
- Sinoeocrinus lui
- Stromatocystites - class Edrioasteroidea
Cnidaria tribe (cnidarians)
- Cambrovitus balangensis - counter-bearing cnidar polyp
- Scenella sp. - was originally placed among the Mollusca
- Sphenothallus taijiangensis
Tribe Lobopodia (Lobopods)
- Microdictyon sp.
Tribe Mollusca (molluscs)
- Haplophrentis carinatus
- Haplophrentis sp.
- Latouchella taijiangensis
- Linevitus opimus
- Rotadiscus guizhouensis
Phylum Porifera (sponges)
- Angulostuspongia conia
- Choiaella ovata
Tribe Priapulida ( priapulida )
- Ottoia sp.
Problematic assignment
- Wiwaxia taijiangensis
Trace fossils
- Gordia marine
- Phycodes coronatum or Treptichnus coronatum
- Phycodes pedum or Treptichnus pedum
- Rusophycus sp.
- Tasmanadia chapman sp.
- Triplexa taijiangensis
See also
swell
- Lin, J. et al .: Silicified egg clusters from a Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale-type deposit, Guizhou, south China . In: Geology . 34, No. 12, 2006, pp. 1037-1040. doi : 10.1130 / B23006A.1 .
- Zhao, Yuanlong, Parsley, Ronald L., Peng, Jin: Middle Cambrian short-stalked eocrinoids from the Kaili Biota: Guizhou Province, China . In: Journal of Paleontology . 82, No. 2, 2008, pp. 415-422. doi : 10.1666 / 06-041.1 .