Potassium telluride
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
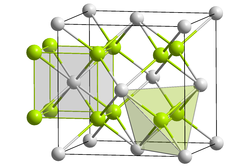
|
||||||||||||||||
| __ Te 2− __ K + | ||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Potassium telluride | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Dipotassium telluride |
|||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | K 2 Te | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
pale yellowish solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 205.80 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
2.52 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Potassium telluride , K 2 Te is an inorganic chemical compound made from tellurium and potassium . In addition to this, with K 2 Te 3 , K 2 Te 2 and K 5 Te 3, further potassium tellurides are known.
Extraction and presentation
Potassium telluride can be obtained by reacting potassium with tellurium in ammonia in the absence of air .
properties
Potassium telluride is a pale yellowish hygroscopic solid that decomposes in air, releasing tellurium. It is soluble in water, the solution decomposing in air, also releasing tellurium.
The cubic crystal structure corresponds to the anti-calcium fluoride type with the space group Fm 3 m (space group no. 225) . Four other crystal structures are known under high pressure and sometimes also at high temperatures.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Wolfgang A. Herrmann, Christian Erich Zybill: Synthetic Methods of Organometallic and Inorganic Chemistry, Volume 4, 1997 Volume 4: Sulfur, Selenium and Tellurium . Georg Thieme Verlag, 2014, ISBN 3-13-179191-8 , p. 191 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Brigitte Eisenmann, Herbert Schäfer: K2Te3: The First Binary Alkali-Metal Polytelluride with Te 2− 3 -Ions. In: Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English. 17, 1978, p. 684, doi : 10.1002 / anie.197806841 .
- ^ I. Schewe, P. Böttcher: Representation and crystal structure of K 5 Te 3 / Preparation and Crystal Structure of K 5 Te 3 . In: Zeitschrift für Naturforschung B. 45, 1990, doi : 10.1515 / znb-1990-0402 .
- ↑ Adolf Pinner: Repetitorium Der Anorganischen Chemie . Рипол Классик, 1885, ISBN 978-5-87746-719-4 , p. 116 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ springer.com: K2Te Crystal Structure - SpringerMaterials , accessed December 30, 2017.
- ↑ K. Stöwe, High-pressure crystal structure investigations on K2Te in DACs of modified Merrill-Bassett type , 2003., Technische Chemie, Universität des Saarlandes, FR 8.1, C4.2, Saarbrücken.
- ↑ Karin Seifert-Lorenz, Jürgen Hafner: Crystalline intermetallic compounds in the K-Te system: The Zintl-Klemm principle revisited. In: Physical Review B. 66, 2002, doi : 10.1103 / PhysRevB.66.094105 .

