Kepler-7
|
Star Kepler-7 |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||
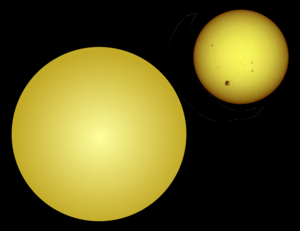
| Schematic size comparison between Kepler-7 (left) and the Sun (right) | |||||
| AladinLite | |||||
|
Observation dates equinox : J2000.0 , epoch : J2000.0 |
|||||
| Constellation | lyre | ||||
| Right ascension | 19 h 14 m 19.6 s | ||||
| declination | + 41 ° 05 ′ 23.3 ″ | ||||
| Typing | |||||
| Known exoplanets | 1 | ||||
| Spectral class | F or G | ||||
| Astrometry | |||||
| Radial velocity | (+0.40 ± 0.10) km / s | ||||
| Physical Properties | |||||
| Dimensions | 1.36 ± 0.03 M ☉ | ||||
| radius | 2.02 ± 0.02 R ☉ | ||||
| Effective temperature | 5933 ± 44 K | ||||
| Metallicity [Fe / H] | 0.11 ± 0.03 | ||||
|
Other names and catalog entries |
|||||
|
|||||
Kepler-7 is a late F or early G-type star that is accompanied by an exoplanet named Kepler-7b . The star appears to be on the main sequence near the end of its life; with a mass of approx. 1.3 solar masses, its radius has expanded to 1.8 solar radii.
Exoplanet
The exoplanet Kepler-7b was performed using the Kepler space telescope of NASA discovered and has a rotation period of 4,886 days. The discovery was announced by the program director, William Borucki, on January 4, 2010 at the American Astronomical Society's annual meeting in Washington . A special feature of the exoplanet is its unusually low density of 0.17 grams per cubic centimeter (for comparison: the earth has a density of 5.515 g / cm³, which is over 30 times higher; the exoplanet has a radius of around 0.4 Jupiter's mass approx. 1.5 radii of Jupiter).
Web links
- Report in SpiegelOnline
- Report on the planet at USNews
- American Astronomical Society homepage
- The exoplanet in the "Encyclopedia of Extrasolar Planets"
Individual evidence
- ↑ Simbad. simbad.u-strasbg.fr, July 31, 2012, accessed on July 31, 2012 .
- ↑ a b c d Kepler-7b. exoplanet.eu, July 31, 2012, accessed July 31, 2012 .