Cloning vector

A cloning vector is a vector which , in contrast to the expression vector , is only used for cloning .
properties
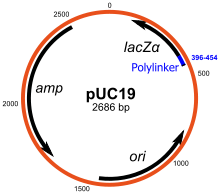
Cloning vectors have an origin of replication for the replication of the DNA, a sequence for the selection of the expression vector (e.g. antibiotic resistance or auxotrophy ) and a polylinker into which a DNA sequence to be cloned (the insert ) is inserted. Cloning vectors in the form of a plasmid are mostly used, but also bacterial artificial chromosomes and λ vectors and M13 vectors . Resistance genes to ampicillin , chloramphenicol , kanamycin and tetracyclines are used as antibiotic resistance .
Cloning vectors are used to propagate the DNA of the insert in bacteria or to change the restriction sites of the insert via the polylinker. The change of the restriction sites by cloning was the first method available for changing the restriction sites, while increasing other methods to change the restriction site such as the primer extension - PCR or restriction-free methods of cloning (eg. TOPO cloning or gateway used cloning) .
literature
- MP Mayer: A new set of useful cloning and expression vectors derived from pBlueScript. In: Genes. Volume 163, Number 1, September 1995, pp. 41-46, PMID 7557476 .
- B. Rohweder, F. Semmelmann, C. Endres, R. Sterner: Standardized cloning vectors for protein production and generation of large gene libraries in Escherichia coli. In: BioTechniques. Volume 64, Number 1, January 2018, pp. 24-26, doi : 10.2144 / 000114628 , PMID 29384074 .
Individual evidence
- ^ Mary Campbell: Biochemistry. Cengage Learning, 2007, ISBN 978-0-495-39041-1 , p. 378.
- ↑ Nicola Casali: E. Coli Plasmid Vectors. Springer Science & Business Media, 2003, ISBN 978-1-592-59409-2 , p. 20.