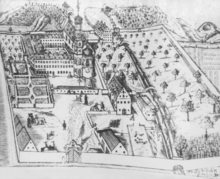
Maihingen Monastery
The monastery Maihingen is a former monastery of the Friars Minor ( Franciscans -Konventualen) in Maihingen in Bavaria in the diocese of Augsburg .
history
The monastery, consecrated to the Immaculate Conception , was founded in 1437 by Johann the Serious, Count of Oettingen , and his family at the suggestion of the Dean Konrad Rösers, pastor of Maihingen, and in 1473 transferred to the Order of Birgit . The monastery economy, but above all the looting and partial destruction of the monastery including the important library during the Peasants' War of 1525 are clearly documented in the records of Prioress Walpurgis Scheffler . From 1607 to 1803 Maihingen was a monastery of the Minorites. In 1802, in the course of secularization, the monastery was transferred to the House of Oettingen-Wallerstein , who took over the property but allowed the Minorites to remain in the monastery. In 1841 the Oettingen-Wallerstein library and art collection were housed in Maihingen . In 1946 the monastery was sold to the Caritas Association and the library moved to Harburg Castle . In 1984, after the retirement home was closed, the Catholic Evangelization Center Maihingen (KEM) was set up in the former convent building. The KEM was renamed Maihingen Monastery in May 2013. The sponsor of the monastery is the Community Lumen Christi e. V.
Baumeister organ
The organ was built into the newly built monastery church by Johann Martin Baumeister ( Eichstätt ) from 1734 to 1737. After secularization in Bavaria , the console was probably sealed in 1803 and the organ was no longer played until the end of the 20th century. Only after a restoration by GF Steinmeiyer ( Oettingen ) between 1988 and 1990 was the organ able to sound again - now with an electric motor for the first time. It sounds in a slightly modified mid-tone tuning .
- Disposition
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-
Pairing :
- Trigger (pedal coupling to the main work)
- Manual slide coupling
Recordings with the baroque organ
- Joseph Kelemen : Organ works by Johann Jacob Froberger on the Baumeister organ (1737) in Maihingen / Ries
- Christian Brembeck : "Gradus ad Parnassum - southern German organ art" - the Baumeister organ (1737) in Maihingen / CANTATE 2009
literature
- From the yearbooks of the Maria Mai im Rieß monastery. Notes of the prioress Walpurgis Schefflerin about the fortunes of her convent in 1525. A source document on the history of the Peasant War in northeastern Swabia. Augsburg 1891.
- Georg Lill (Ed.), Karl Gröber: Die Kunstdenkmäler von Bayern, VII (Swabia), 1: District Office Nördlingen . R. Oldenbourg Verlag, Munich 1938, pp. 268-291. (Reprint: R. Oldenbourg Verlag, Munich / Vienna 1982, ISBN 3-486-50514-9 ). [not evaluated]
Web links
- Website of the Maihingen Monastery
- Maihingen Monastery , basic data in the database of monasteries in Bavaria in the House of Bavarian History
Individual evidence
- ↑ Georg Schwaiger: Monasticism, orders, monasteries. CH Beck, 2003, ISBN 978-3-406-49483-3 , p. 118. Limited preview in the Google book search
- ↑ Joseph Kelemen : The master builder organ of the monastery church Maihingen . In: The most beautiful organs 2013 . St. Benno-Verlag, Leipzig 2012, ISBN 978-3-7462-3273-7
Coordinates: 48 ° 55 ′ 42.2 " N , 10 ° 29 ′ 29.6" E