Conjunction (astronomy)
As a conjunction ( astronomical symbols : ☌) is the apparent encounter between two planets called or a planet with sun or moon, d. H. an elongation of 0 °. It occurs when the celestial bodies in the starry sky reach the same coordinate value of the right ascension . Sometimes it is also related to the ecliptical length ( conjunction in length ). The smaller the coordinate difference in declination , the closer the celestial bodies are to each other.
If one of the bodies pushes itself in front of the other in very close encounters, one speaks of touch or covering . As contact the moments are referred to, where the visible slices touch from outside or inside.


Points in time
Conjunction in right ascension , in declination and touch are apart in time in general. It is possible that two celestial bodies come in conjunction in ecliptical length (but not in right ascension), and vice versa. If the angular distance between the two celestial bodies falls below the sum of the apparent radii , there is contact . Depending on whether the smaller or the larger body is closer to the observer, i.e. which of the two is “in front”, one speaks of passage (transit) or occultation (covering) .
While the conjunctions of planets take place every synodic period , touching or covering between them is extremely rare. Planetary occultations by the moon, on the other hand, occur more frequently because of its apparent size - on average several per decade. In contrast, star occultations that are visible to the naked eye occur about weekly.
At the edge of the sun or moon, four selected points in time are then designated as 1st - 4th contact :
- The first and fourth contact is the moment when the edges of the celestial bodies touch, but the center of the smaller body is still or is already outside the disk of the larger one.
- The second and third contact are the points in time of the edge contact at which the passage already takes place.
See also solar eclipse , edge of the sun , star cover .
All three phenomena are generally related to an observer on earth, but could also be defined for any other viewpoint ( topocentric problem). Then these events take place at times other than for Earth.
Special conjunctions
Conjunctions between the planets with each other, the planets and bright fixed stars , the moon and planets, as well as the moon and bright stars often create interesting sights. They are therefore usually listed in astronomical yearbooks. Sometimes planets also form triangles or squares with bright stars for a few days to weeks , but this is not calculated in advance. At the spring sky in 2014 there were two such constellations: Jupiter with the twin stars Castor and Pollux, and Mars, Saturn, Arcturus and Spica in Virgo.
The meeting of Jupiter and Saturn in the sky, which is known as the Great Conjunction , is particularly spectacular . It occurs about every 20 years. Because the two bright planets move slowly across the starry sky because of their great distance, they stand close together for weeks. If they have their opposition during this time , their annual planetary loops can almost coincide, and they even meet three times during a few months . This rare special case is called Greatest Conjunction ; its appearance in the year 6 BC Chr. Is considered the most conclusive explanation of the star of Bethlehem described in the Gospel of Matthew .
Conjunctions of minor planets (asteroids) or the faint planets Uranus and Neptune with bright planets or fixed stars enable even inexperienced observers to seek out these objects, since the bright planet or star can serve as a guide star.
Interesting conjunctions also result from the passage of satellites , but require very precise precalculation and special methods of observation .
Star coverings by asteroids make it possible to measure their size and shape very precisely by measuring the occultation duration and time at different locations on earth.
Planetary conjunctions
Triple conjunction and loop
If two celestial bodies are in opposition to the sun at almost the same time , three conjunctions can occur within a few months because of the apparent loop paths of the celestial bodies involved. One speaks of a threefold conjunction . Such events are very rare between planets. The last such triple conjunction between Mars and Jupiter took place in 1980, between Jupiter and Saturn in 1981 and between Mars and Saturn in 1945/46, the next such events only occur again in 2123 (triple conjunction Mars - Jupiter), 2238/39 (triple conjunction Jupiter - Saturn) and 2148 (triple conjunction Mars - Saturn). Triple conjunctions between Jupiter and Uranus and Jupiter and Neptune are more common.
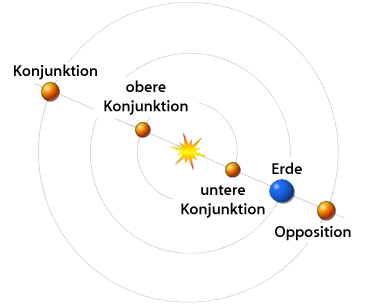
Upper and lower conjunction
For the lower planets Mercury and Venus , the term upper conjunction and lower conjunction is used in connection with conjunctions with the sun . If Mercury and Venus are behind the sun - seen from the earth - they are in the upper conjunction, if they are between the sun and the earth they are in the lower conjunction. The two planets have the greatest earth distance in the upper conjunction, and the smallest earth distance in the lower conjunction, but are only visible in exceptional cases (Mercury and Venus during a passage or Venus when the northern or southern solar distance is large).
For the upper planets there is only one type of conjunction with the sun (behind this, they cannot stand between earth and sun). If an upper planet is in conjunction, it has the maximum distance from the earth and is invisible from earth. The upper planets achieve their best visibility at the time of opposition .
Conjunctions of the moon
If the moon is in conjunction with the sun, we have a new moon . Like Mercury and Venus, the moon usually passes north or south of the sun. Only when it is close to its orbit does it pass directly in front of the sun for observers in some areas of the earth. A partial or total solar eclipse takes place there.
See also
Special forms of conjunction
Other special constellations
- opposition
- quadrature
- Sextile
- Trine
- Quasi-conjunction
Individual evidence
- ↑ Aspects (lexicon entry). In: Meyers Großes Konversations-Lexikon. 6th edition, Bibliographisches Institut, Leipzig / Vienna 1905-1909. 1909, Retrieved July 23, 2018 .
- ↑ For example 45 in 2016 for Vienna and Munich (according to the Austrian sky calendar 2016)