Crab mongoose
| Crab mongoose | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Crab mongoose (museum specimens) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Herpestes urva | ||||||||||||
| ( Hodgson , 1836) |
The crab mongoose ( Herpestes urva ) is a species of predator from the mongoose family (Herpestidae). It occurs in Southeast Asia and is characterized by a light neck stripe.
features
The crab mongoose is a relatively large mongoose. It reaches a head body length of about 44–56 cm, the tail measures 26.5–34 cm. The weight is around 3–4 kg. The basic color is gray to black-brown, with the individual hairs being curled light and dark. The top hair is quite long (about 4–5 cm on the back). Characteristic are a whitish, 8–9 cm long neck stripe, a white chin, a greyish throat and a dark chest area. The legs are also dark in color, but the belly is relatively light. The top of the head is speckled with white, the muzzle pale yellow. There are two cherry-sized anal glands on either side of the anus. The dentition consists of 40 teeth.
Tooth formula:
Subspecies
There are four subspecies of the crab mongoose:
- H. u. urva ( Hodgson , 1836) - Nepal to Indochina and the Malay Peninsula
- H. u. annamensis ( Bechtold , 1936) - Vietnam
- H. u. formosanus ( Bechtold , 1936) - Taiwan
- H. u. sinensis ( Bechtold , 1936) - South China and Hainan
distribution and habitat
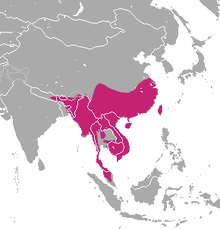
The crab mongoose inhabits evergreen and deciduous forests, scrub areas, wetlands and plantations. They are often found near bodies of water, such as ponds and rivers. The distribution area extends over large parts of Southeast Asia and extends from Nepal and southern China to the Malay Peninsula. It is also found on the islands of Taiwan and Hainan. In some areas, such as Taiwan and Laos , the crab mongoose is hunted as a source of meat. She is also being persecuted for her fur. Nevertheless, the crab mongoose is relatively common and is classified by the IUCN as not endangered (" Least Concern ").
Way of life
The crab mongoose is a typical omnivore and has a very varied diet. For example, most of the diet in northern Thailand consists of crustaceans (28%) and insects (29%). Amphibians, reptiles, mollusks and worms also make up a large part of the diet. In contrast, rodents also appear to be important prey in southern China, for example. Obviously birds, fish and fruits are less important. Overall, relatively little is known about the way of life. Crab mongooses are reputed to be good swimmers and divers, which would benefit them when hunting crabs and other aquatic animals. Most of the time, however, they move on solid ground on the ground. The animals usually live solitary, but small groups of up to four animals are sometimes seen. These mongooses seem to be both diurnal and nocturnal. During the rest phases, they apparently look for hiding places, such as caves in the earth. The gestation period is 50–63 days. A litter consists of two to four boys.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d J. S. Gilchist, AP Jennings, G. Veron, & P. Cavallini (2009). Family Herpestidaae (Mongooses). In: Don E. Wilson, Russell A. Mittermeier (eds.): Handbook of the Mammals of the World. Volume 1: Carnivores. Lynx Edicions, 2009, ISBN 978-84-96553-49-1 , (pp. 311 f.).
- ↑ Herpestes urva in the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2011.1. Listed by: Duckworth, JW & Timmins, RJ, 2008. Retrieved November 27, 2011.