Lobectomy
With the term lobectomy ( ancient Greek λοβός Lobos "rag" and ἐκτομή ektomế "cutting out"), even Lappenresektion called, is known in the surgery , the surgical removal of an organ lobe.
description
The main organs for a lobectomy are the lungs , the liver , the thyroid gland and the cerebrum .
Lobectomy of the lungs
The most common lobectomies are performed on the lungs , which is why the term lobectomy is often used synonymously in the literature for the surgical removal of a lung lobe. The human lungs have three lobes on the right (right lung) and two on the left (left lung). Removing a lobe from the lung is called a lobectomy. If, on the other hand, two adjacent lobes are removed from the right lung, this is called a bilobectomy . The removal of an entire lung is called a pneumectomy or pneumonectomy .
Since the individual lung lobes are surrounded by a separate pleural layer , only comparatively small wound areas are created on the lungs when a lung lobe is removed. The free space in the chest that arises after the removal of the lobe is compensated for by overstretching the remaining lung, stepping up the diaphragm and shifting the mediastinum . In the case of bronchial carcinoma (lung cancer), the lobectomy is the most frequently performed surgical procedure to remove the primary tumor . For peripheral malignant tumors of tumor classes T1 and T2 (<5 cm maximum tumor size), lobectomy is the surgical procedure of choice. A lobectomy of the lungs is a serious procedure. In spite of significant surgical advances, the operative lethality in the classic open lobectomy is 1 to 4%. In an open lobectomy, the chest is opened with a large incision. The pain is considerable, and the patients operated on in this way are usually in the hospital for at least one week after the operation. In the minimally invasive VATS -Lobektomie (VATS = video-assisted thoracic surgery , patients can = video-assisted thoracic surgery) often just two days after surgery, the clinic abandoned, the pain is significantly lower. However, the possibility of a VATS lobectomy is linked to certain boundary conditions that go beyond the standard criteria for a lobectomy. For example, the ability to tolerate one lung ventilation must also be given. The maximum tumor size must be less than 5 cm, there must be no extensive pleural adhesions and the tumor must not have any connection (surgically referred to as a relationship ) to the lung hilum . In addition, there are contraindications such as obesity or chemotherapy or radiation therapy before the procedure ( neoadjuvant therapy ).
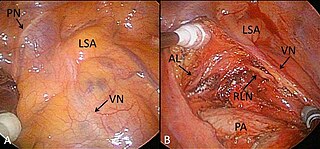
Single-port video-assisted thoracoscopy (VATS) for lung lobectomy. Video image during the operation from the lower left mediastinum .
Liver lobectomy
Removal of a lobe of the liver is a partial resection of the liver called a lobectomy of the liver. In contrast to hemihepatectomy , the liver is divided anatomically. In a left-sided lobectomy, for example, the left lobe only includes the parenchyma , which lies to the left of the falciforme hepatis ligament (sickle-shaped liver ligament ), while in a left-sided hemihepatectomy two segments (IVa and IVb) of the right liver lobe are also removed.
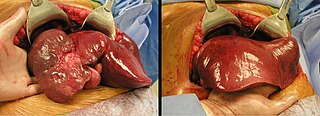
Image of a lobectomy to remove a hepatocellular adenoma on the left lobe of the liver.
Thyroid lobectomy
The complete removal of one of the two lobes of the thyroid gland is known as a hemithyroidectomy (Greek ἡμισ = hemi = 'half') or a lobectomy of the thyroid gland. The operation can be classically open (picture 1) or minimally invasive (picture 2).
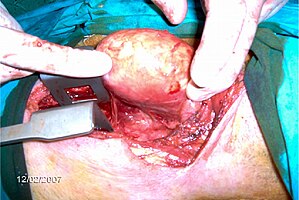
A left-sided lobectomy of the thyroid gland after sternotomy to remove a calcified capsule on the left lobe of the thyroid.
Cerebral lobectomy
The partial or complete removal of a cerebral lobe is a neurosurgical procedure that is used primarily to treat refractory epilepsy , i.e. epilepsy that does not respond to commonly used drugs. A distinction is made between one
- bilateral lobectomy: removal of one (partial) cerebral lobe, both in the right and left cerebral hemisphere and one
- Temporal lobectomy: bilateral or unilateral, complete or partial removal of a temporal lobe .
The most famous case study of a lobectomy on the cerebrum is the patient Henry Gustav Molaison , usually referred to as HM in the literature . For the treatment of his severe epilepsy, a bilateral mediotemporal lobectomy was performed, that is, parts of the temporal lobe in the middle were removed. His case was a milestone in memory research.
Cerebral lobectomy can also serve as a last resort (last resort) for intracranial pressure lowering ( decompressive lobectomy are used).
further reading
- K. Kim: Video-assisted Thoracic Surgery Lobectomy. In: The Korean journal of thoracic and cardiovascular surgery. Volume 44, Number 1, February 2011, pp. 1-8, ISSN 2093-6516 . doi : 10.5090 / kjtcs.2011.44.1.1 . PMID 22263117 . PMC 3249267 (free full text).
- D. Schneiter, W. Weder: Minimally invasive surgery for bronchial carcinoma: possibility and limits. In: Therapeutic review. Volume 69, Number 7, July 2012, pp. 406-410, ISSN 0040-5930 . doi : 10.1024 / 0040-5930 / a000307 . PMID 22753289 . (Review).
- S. Jheon, HC Yang, S. Cho: Video-assisted thoracic surgery for lung cancer. In: General thoracic and cardiovascular surgery. Volume 60, Number 5, May 2012, pp. 255-260, ISSN 1863-6713 . doi : 10.1007 / s11748-011-0898-6 . PMID 22453533 . (Review).
- S. Yendamuri, TL Demmy: Lobectomy for patients with limited lung function. In: Seminars in thoracic and cardiovascular surgery. Volume 23, Number 3, 2011, pp. 191-195, ISSN 1532-9488 . doi : 10.1053 / j.semtcvs.2011.09.004 . PMID 22172355 . (Review).
- L. Solaini, F. Prusciano et al. a .: Video-assisted thoracic surgery (VATS) of the lung: analysis of intraoperative and postoperative complications over 15 years and review of the literature. In: Surgical endoscopy. Volume 22, Number 2, February 2008, pp. 298-310, ISSN 1432-2218 . doi : 10.1007 / s00464-007-9586-0 . PMID 17943372 . (Review).
- E. Chaib, MA Ribeiro et al. a .: Anterior hepatic transection for caudate lobectomy. In: Clinics. Volume 64, Number 11, 2009, pp. 1121-1125, ISSN 1980-5322 . doi : 10.1590 / S1807-59322009001100013 . PMID 19936187 . PMC 2780530 (free full text). (Review).
- E. Chaib, MA Ribeiro et al. a .: Caudate lobectomy: tumor location, topographic classification, and technique using right- and left-sided approaches to the liver. In: The American Journal of Surgery . Volume 196, Number 2, August 2008, pp. 245-251, ISSN 1879-1883 . doi : 10.1016 / j.amjsurg.2007.11.020 . PMID 18571618 . (Review).
- ZA Memon, G. Ahmed et al. a .: Postoperative use of drain in thyroid lobectomy - a randomized clinical trial conducted at civil hospital, Karachi, Pakistan. In: Thyroid research. [Electronic Publication Before Press] Issue 1, Sep 2012, ISSN 1756-6614 . doi : 10.1186 / 1756-6614-5-9 . PMID 23021778 .
- JK Byrd, RJ Yawn, et al. a .: Well differentiated thyroid carcinoma: current treatment. In: Current Treatment Options in Oncology . Volume 13, Number 1, March 2012, pp. 47-57, ISSN 1534-6277 . doi : 10.1007 / s11864-011-0173-1 . PMID 22234582 . (Review).
- JS Cho, JH Yoon et al. a .: Observational study of central metastases following thyroid lobectomy without a completion thyroidectomy for papillary carcinoma. In: Journal of the Korean Surgical Society. Volume 83, Number 4, October 2012, pp. 196-202, ISSN 2093-0488 . doi : 10.4174 / jkss.2012.83.4.196 . PMID 23091791 . PMC 3467385 (free full text).
- VL Ives-Deliperi, JT Butler: Naming outcomes of anterior temporal lobectomy in epilepsy patients: a systematic review of the literature. In: Epilepsy & behavior. Volume 24, Number 2, June 2012, pp. 194-198, ISSN 1525-5069 . doi : 10.1016 / j.yebeh.2012.04.115 . PMID 22569529 . (Review).
- L. Bonilha, GU Martz u. a .: Subtypes of medial temporal lobe epilepsy: influence on temporal lobectomy outcomes? In: Epilepsia. Volume 53, Number 1, January 2012, pp. 1-6, ISSN 1528-1167 . doi : 10.1111 / j.1528-1167.2011.03298.x . PMID 22050314 . (Review).
- S. Pati, AV Alexopoulos: Pharmacoresistant epilepsy: from pathogenesis to current and emerging therapies. In: Cleveland Clinic journal of medicine. Volume 77, Number 7, July 2010, pp. 457-467, ISSN 1939-2869 . doi : 10.3949 / ccjm.77a.09061 . PMID 20601619 . (Review).
Individual evidence
- ^ A b Burkhard Paetz: Surgery. 21st edition, Georg Thieme Verlag, 2009, ISBN 3-13-332921-9 , p. 273. Restricted preview in the Google book search
- ↑ L. Sunder-Plassmann, C. Schuhmann: Malignant lung tumors. In: Jörg Rüdiger Siewert: Practice of Visceral Surgery. 3rd edition, Verlag Springer, 2010, ISBN 3-642-03807-7 , p. 433. Restricted preview in the Google book search
- ↑ L. Sunder-Plassmann, C. Schuhmann: Malignant lung tumors. In: Jörg Rüdiger Siewert: Practice of Visceral Surgery. 3rd edition, Verlag Springer, 2010, ISBN 3-642-03807-7 , p. 426. Restricted preview in the Google book search
- ↑ VATS lobectomy / VATS lobectomy. ( Memento of the original from January 7, 2010 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. University Hospital Erlangen, accessed on January 2, 2013
- ↑ Peter Drings, Hendrik Dienemann, Michael Wannenmacher: management of lung cancer. Springer, 2003, ISBN 3-540-43145-4 , p. 248. Limited preview in the Google book search
- ↑ H. Wada, Y. Hida et al. a .: Video-assisted thoracoscopic left lower lobectomy in a patient with lung cancer and a right aortic arch. In: Journal of cardiothoracic surgery. Volume 7, 2012, p. 120, ISSN 1749-8090 . doi: 10.1186 / 1749-8090-7-120 . PMID 23147195 . PMC 3527347 (free full text).
- ^ CH Chen, SY Lee et al. a .: Technical aspects of single-port thoracoscopic surgery for lobectomy. In: Journal of cardiothoracic surgery. Volume 7, 2012, p. 50, ISSN 1749-8090 . doi: 10.1186 / 1749-8090-7-50 . PMID 22672719 . PMC 3431998 (free full text).
- ↑ Volker Schumpelick: Surgery Atlas. 2nd edition, Georg Thieme Verlag, 2006, ISBN 3-131-40632-1 , p. 231. Restricted preview in the Google book search
- ↑ Andreas Hirner, Kuno Weise: Surgery: cut by cut. Georg Thieme Verlag, 2004, ISBN 3-131-30841-9 , p. 523. Restricted preview in the Google book search
- ↑ Felix Braun, Thomas Becker and others: Liver. In: Doris Henne-Bruns: Dual series surgery. 4th edition, Georg Thieme Verlag, 2012, ISBN 3-131-51314-4 , p. 479. Restricted preview in the Google book search
- ↑ SA Gulec, K. Pennington u. a .: Preoperative Y-90 microsphere selective internal radiation treatment for tumor downsizing and future liver remnant recruitment: a novel approach to improving the safety of major hepatic resections. In: World journal of surgical oncology. Volume 7, 2009, p. 6, ISSN 1477-7819 . doi : 10.1186 / 1477-7819-7-6 . PMID 19133156 . PMC 2655298 (free full text).
- ↑ L. Sandonato, C. Cipolla et al. a .: Giant hepatocellular adenoma as cause of severe abdominal pain: a case report. In: Journal of medical case reports. Volume 1, 2007, p. 57, ISSN 1752-1947 . doi : 10.1186 / 1752-1947-1-57 . PMID 17662116 . PMC 1950307 (free full text).
- ^ Burkhard Paetz, Brigitte Benzinger-König: Surgery for nursing professions. 20th edition, Georg Thieme Verlag, 2004, ISBN 3-133-32920-0 , p. 243. Restricted preview in the Google book search}
- ↑ MF Yuzbasioglu, M. Ozkaya et al. a .: Eggshell calcification after intrathyroidal hemorrhage of retrosternal thyroid. In: Cases journal. Volume 1, Number 1, 2008, p. 11, ISSN 1757-1626 . doi : 10.1186 / 1757-1626-1-11 . PMID 18577251 . PMC 2438315 (free full text).
- ↑ N. Irawati: Endoscopic right lobectomy axillary-breast approach: a report of two cases. In: International journal of otolaryngology. Volume 2010, 2010, pp. 958764, ISSN 1687-921X . doi : 10.1155 / 2010/958764 . PMID 21253488 . PMC 3022208 (free full text).
- ↑ a b Clemens Kirschbaum: Compendium Biopsychology. Springer, 2008, ISBN 3-540-39603-9 , p. 169. Restricted preview in the Google book search
- ^ M. Brand, HJ Markowitsch: Memory disorders. In: language, voice, hearing. Volume 27, Number 1, 2003, pp. 11-17. doi : 10.1055 / s-2003-37877
- ↑ Harald Barth, Ralph Schön: Neurosurgery. In: Doris Henne-Bruns: Dual series surgery. 4th edition, Georg Thieme Verlag, 2012, ISBN 3-131-51314-4 , p. 1138. Restricted preview in the Google book search