Mesyl group

The covalently bonded residue of methanesulfonic acid is referred to as the mesyl group (CH 3 SO 2 -) - also methanesulfonyl group. These are the esters of methanesulfonic acid. The name derives from its systematic name Me than s ulfon yl off. The compounds are usually referred to as mesylates are described and distinguished from the salts of methanesulfonic acid ( mesilates ). In structural formulas, the mesyl group is sometimes abbreviated to Ms or Mes. It is structurally related to the triflyl group.
Manufacturing
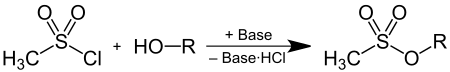
Mesylates can be made by the reaction of methanesulfonyl chloride with alcohols in the presence of bases :
properties
Methanesulfonic acid is one of the strong acids . The mesylation ion is therefore a weak base, which is well stabilized by mesomerism :
For this reason, the mesyllate group is a good leaving group, which can easily be split off with substitution by suitable nucleophiles . Alkyl mesylates are good alkylating agents . Because of their ability to alkylation of DNA , the Mesylverbindungen apply Methansulfonsäureallylester , methanesulfonate and methyl methanesulfonate as potential carcinogens .
use
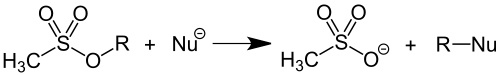
In its capacity as a leaving group, the mesylate group is used in preparative organic chemistry . By converting alcohols into mesylates, the poor leaving group OH - is converted into a good leaving group CH 3 SO 3 - , which enables nucleophilic substitution reactions at this position:
This application is not particularly atom-economical , since stoichiometric amounts of waste materials with a comparatively high molecular mass are always formed. This is why the synthesis method is mainly used on a laboratory scale and rarely in technical processes.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b H. P. Latscha, U. Kazmaier, HA Klein: Organische Chemie: Chemie-Basiswissen II , 6th Edition, 2008, p. 173, Springer, Berlin, ISBN 3-540-77106-9 .
- ↑ Entry on methanesulfonic acid. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on September 29, 2014.