Mojave rattlesnake
| Mojave rattlesnake | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Mojave rattlesnake ( Crotalus scutulatus ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Crotalus scutulatus | ||||||||||||
| Kennicott , 1859 |
The Mojave rattlesnake ( Crotalus scutulatus ) is a species of rattlesnake ( Crotalus ) whose range extends from the Mojave Desert in southern California and Nevada via Arizona to Mexico . It is often regarded as one of the most dangerous rattlesnake species due to its highly potent venom and the relatively frequent bite accidents.
features
The Mojave rattlesnake is a medium-sized rattlesnake with a maximum body length of about one meter. The typical basic color is greenish, olive green, brown, yellow-brown or yellow with angled spots on the back. As a rule, the spots are well delimited from one another and clearly recognizable, which means that they can be distinguished very well from the Texas rattlesnake ( C. atrox ), with which it is often confused. The tail has black and white stripes, with the white stripes being significantly wider than the black.
distribution and habitat
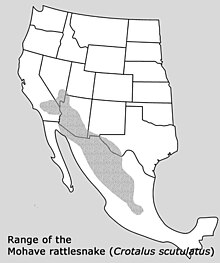
The range of the snake stretches from the Mojave Desert in southern California and Nevada over Arizona to Mexico and there to the south of the states of Puebla and Veracruz .
The habitat of the snake is characterized in the north by dry sandy deserts (Mojave). In the south, however, it lives in stony, but also very dry areas. While it is considered a lowland species in the north, it occurs in Mexico up to an altitude of 2,500 meters.
Snake venom
The poison consists, among other things, of two very different components with different effects, whereby the proportions vary regionally. Like other North American rattlesnakes, it has a haemotoxic venom that mainly contains tissue-destroying proteins. The effect consists mainly of tissue destruction, local painful swellings and hemorrhagic effects. In addition, there are highly potent neurotoxic components that act on the central nervous system and lead to paralysis, shock, failure of nerve supplies to central organs and kidney failure.
Systematics
Two subspecies of the Mojave rattlesnake are currently considered valid:
- C. s. salvini in the southernmost areas of the distribution area in Tlaxcala , Puebla and Veracruz
- C. s. scutulatus in the United States as well as most of the Mexican range.
literature
- Chris Mattison: Rattlers! - A natural history of rattlesnakes. Blandford, London 1996, ISBN 0-7137-2534-6 , p. 121.
Web links
- Crotalus scutulatus in The Reptile Database
- Crotalus scutulatus inthe IUCN 2013 Red List of Threatened Species . Listed by: Mendoza-Quijano, F. & Hammerson, GA, 2007. Retrieved October 5, 2013.