Moor diaper snail
| Moor diaper snail | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
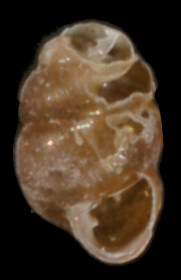
Moor diaper snail ( Vertigo lilljeborgi ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Vertigo lilljeborgi | ||||||||||||
| ( Westerlund , 1871) |
The Moor's whorl snail ( Vertigo lilljeborgi ), also moorland whorl snail called, is a snail of the family of vertiginidae (Vertiginidae) from the subordination of terrestrial snails (gastropod).
features
The right-hand wound, egg-shaped case is 1.7 to 2.05 mm high and 1.15 to 1.35 mm wide. It has 4 to 5 strongly arched, rapidly increasing turns with a deep seam. The last turn is comparatively very large and bulbous; it rises only a little towards the mouth. The edge of the mouth is hardly thickened, tapered rather sharply and only very slightly expanded. The ornamentation consists of weak but regular growth strips. The mouth is pear-shaped to crooked heart-shaped when viewed from the front. It is usually reinforced with four well-formed, slender teeth: a parietal tooth, a columellar tooth and two palatal teeth. The teeth set off directly from the inner wall of the mouth. The neck bulge is only weakly developed.
The housing is yellowish-brown to brown in color, the surface is shiny. The shell is thin and fragile.
Similar species
The outer habitus of the species is very similar to the bellied diaper snail ( Vertigo moulinsiana ). However, it is significantly smaller than this. However, it differs in the genital apparatus. The common diaper snail ( Vertigo pygmaea ) is similar in size to the moor diaper snail, but significantly slimmer. All three types show a similar reinforcement of the mouth. In the common diaper snail and the bellied diaper snail, the teeth at the base are connected by a callus.
Geographical distribution and habitat
The distribution area extends from Ireland, Northern England and Scotland via Scandinavia, the Baltic States (Latvia) to northwestern Russia. But there are also isolated populations in Wales, Denmark, Germany (e.g. Black Forest, Bavarian Forest, etc.), the Czech Republic, France (Auvergne) and in the French and Spanish Pyrenees. A deposit was also recently discovered in the Altai .
The animals live in open swamps, in alder quarries, on the edges of ponds and brooks, often in the floodplain area in damp, rotting plant remains. They prefer low-mineral, rather acidic soils.
Taxonomy
The taxon was first described in 1871 by Carl Agardh Westerlund as Pupa lilljeborgi .
Danger
The species is extremely rare in Germany (hazard category R). In other European countries, the species is partly endangered by drainage and hydraulic engineering. In England and Ireland some populations have been destroyed in the last few decades. In Ireland it is classified as “vulnerable” (“at risk”). The International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) rates the degree of endangerment as a whole as “Near Threatened” (low risk).
supporting documents
literature
- Rosina Fechter and Gerhard Falkner: molluscs. 287 p., Mosaik-Verlag, Munich 1990 (Steinbach's Nature Guide 10) ISBN 3-570-03414-3 (p. 140)
- Michael P. Kerney, RAD Cameron & Jürgen H. Jungbluth: The land snails of Northern and Central Europe. 384 pp., Paul Parey, Hamburg & Berlin 1983 ISBN 3-490-17918-8 (p. 90)
- Ted von Proschwitz: On the distribution and ecology of Vertigo substriata (Jeffreys), Vertigo modesta artica (Wallenberg), Vertigo lilljeborgi (Westerlund) and Vertigo alpestris Alder in France and on the Iberian Peninsula. Journal of Conchology, 38 (4): 411-420.
- Francisco W. Welter-Schultes: European non-marine molluscs, a guide for species identification = identification book for European land and freshwater mollusks. A1-A3 S., 679 S., Q1-Q78 S., Göttingen, Planet Poster Ed., 2012 ISBN 3-933922-75-5 , ISBN 978-3-933922-75-5
Individual evidence
- ↑ Vertigo lilljeborgi (Westerlund) in Latvia (in Latvian)
- ^ Vertigo lilljeborgi - Another Glacial Relict. From the Red Book of Czech Molluscs
- ↑ Benoît Lecaplain: Découverte du Vertigo des aulnes, Vertigo lilljeborgi (Westerlund, 1871) (Gastropoda, Vertiginidae) dans la region Auvergne (France). MalaCo, 9: 2 S., 2012 PDF ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Stefan Meng: New data on the distribution of the Vertiginidae (Gastropoda: Pulmonata) in Central Asia. Mollusca, 26 (2): pp. 207-219, Dresden 2008 PDF
- ↑ Carl Agardg Westerlund: Expose critique of Mollusques de terre et d'eau douce de la Suède et de la Norvége. Pp. 1–200, Upsala, Berling 1871 Online at Google Books (p. 90).
- ^ JH Jungbluth, D. von Knorre (with the assistance of U. von Bössneck, K. Groh, E. Hackenberg, H. Kobialka, G. Körnig, H. Menzel-Harloff, H.-J. Niederhöfer, S. Petrick, K. Schniebs, V. Wiese, W. Wimmer, ML Zettler): Red list of internal mollusks [snails (Gastropoda) and mussels (Bivalvia)] in Germany. Announcements of the German Malacoological Society, 81: 1-28, Frankfurt / M. 2009 PDF ( Memento of the original from June 16, 2013 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (1.3 MB)
- ↑ Ireland Red List No. 2 Non-Marine Molluscs 2009 PDF
- ^ Neubert, E. 2011. Vertigo lilljeborgi. In: IUCN 2013. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2013.1. <www.iucnredlist.org>. Retrieved August 7, 2013