NaK (alloy)
NaK is the name of an alloy that consists of sodium and potassium and forms a eutectic , i.e. H. the mixtures of the two components have a lower melting point than that of the pure substances. It is liquid in a wide range of concentrations at room temperature and has occasionally been used to cool nuclear reactors .
properties
Physical Properties
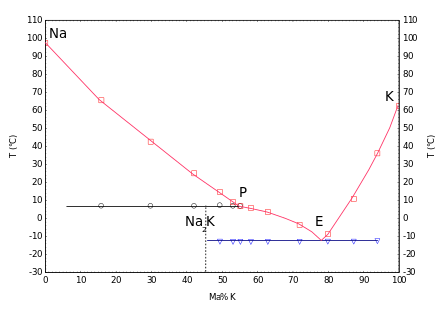
(Na: pure sodium, K: pure potassium, E: eutectic , P: peritectic , blue: eutectic mixture, black: Na 2 K, incongruent melt, red: excess component)
NaK mixtures with a potassium content of 45% to 89% are liquid at room temperature. The eutectic is present at a concentration of 22% sodium and 78% potassium. It has a melting point of −11 ° C and a boiling point of 785 ° C. The density of the alloy is 0.866 g / cm³ (at 21 ° C) lower than that of water. The interfacial tension is very high, so that the liquid tends to form large droplets.
Chemical properties
Like its components sodium and potassium, NaK reacts very easily with water and oxygen. When stored in air, a layer of yellow potassium hyperoxide forms , which is fire-promoting. Since it consists of alkali metals, it has a strong reducing effect .
Other alloys
Other very low melting temperatures have Cs 77 K 23 with −37.5 ° C, Cs 95 Na 5 with −30 ° C and Na 8 Rb 92 with −5 ° C. The alloy of 11.8% sodium, 47.4% potassium and 40.8% cesium has an even lower melting temperature of −79.4 ° C.
Manufacturing
Industrially, NaK is produced by distillation . Liquid sodium and potassium chloride are continuously fed to a distillation column. In the reaction zone, the potassium chloride reacts with the sodium, so that sodium chloride and potassium are formed. In the rectifying section of the column above, the lower-boiling potassium is enriched and taken off overhead as a mixture with sodium in any concentration.
use
Coolant in nuclear reactors
NaK can be used to cool nuclear reactors that work with fast neutrons . The low melting point eliminates the need for external heating to keep the coolant liquid when the reactor is shut down. The Soviet RORSAT satellites used a nuclear reactor with NaK cooling as an energy source.
Chemical process
NaK can be used as a catalyst in various reactions, such as B. in the production of ibuprofen . When mixed with water, hydrogen is created (water splitting).
Desiccant
Due to its high reactivity with water and its liquid state, NaK can be used as a dehydrating agent to remove residual moisture from solvents such as ethers, for example. B. tetrahydrofuran to be separated.
Individual evidence
- ↑ GLCM van Rossen, H. van Bleiswijk: About the state diagram of the potassium-sodium alloys , in: Z. anorg. allg. Chem. , 1912 , 74 , pp. 152-156. doi : 10.1002 / zaac.19120740115
- ↑ MSDS (PDF; 21 kB) Callery Chemical Company, January 3, 2000
- ↑ Jackson, CB; Werner, RC: The Manufacture of Potassium and NaK In: Advances in Chemistry, Vol. 19, January 1, 1957 doi : 10.1021 / ba-1957-0019.ch018
- ↑ Manfred Klell, Helmut Eichlseder, Alexander Trattner: Hydrogen in vehicle technology: generation, storage, application , Springer-Verlag 2018, 324 pages, page 103
